Telmisartan Mitigates TNF-α-Induced Type II Collagen Reduction by Upregulating SOX-9
- PMID: 34056329
- PMCID: PMC8154015
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c01170
Telmisartan Mitigates TNF-α-Induced Type II Collagen Reduction by Upregulating SOX-9
Abstract
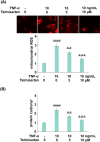
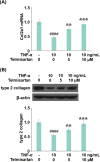
The proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)-induced degradation of extracellular matrix (ECM), such as type II collagen in chondrocytes, plays an important role in the development of osteoarthritis (OA). Telmisartan, an angiotensin II (Ang-II) receptor blocker, is a licensed drug used for the treatment of hypertension. However, the effects of Telmisartan in tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)-induced damage to chondrocytes and the progression of OA are unknown. In this study, we found that treatment with Telmisartan attenuated TNF-α-induced oxidative stress by reducing the levels of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the production of protein carbonyl in human C28/I2 chondrocytes. Interestingly, Telmisartan inhibited TNF-α-induced expression and secretions of proinflammatory mediators such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1). Notably, stimulation with TNF-α reduced the levels of type II collagen at both the mRNA and the protein levels, which was rescued by the treatment with Telmisartan. Mechanistically, we found that Telmisartan restored TNF-α-induced reduction of SOX-9. Silencing of SOX-9 blocked the inhibitory effects of Telmisartan against TNF-α-induced degradation of type II collagen. These findings suggest that Telmisartan might be a potential and promising agent for the treatment of OA.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced interleukin-6 expression by telmisartan through cross-talk of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma with nuclear factor kappaB and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-beta.Hypertension. 2009 May;53(5):798-804. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.126656. Epub 2009 Mar 16. Hypertension. 2009. PMID: 19289654
-
Ivabradine abrogates TNF-α-induced degradation of articular cartilage matrix.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Jan;66:347-353. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.11.035. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30521963
-
Feprazone Ameliorates TNF-α-Induced Loss of Aggrecan via Inhibition of the SOX-4/ADAMTS-5 Signaling Pathway.ACS Omega. 2021 Mar 12;6(11):7638-7645. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c06212. eCollection 2021 Mar 23. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 33778274 Free PMC article.
-
The role of cytokines in osteoarthritis pathophysiology.Biorheology. 2002;39(1-2):237-46. Biorheology. 2002. PMID: 12082286 Review.
-
Effects of telmisartan therapy on interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Hypertens Res. 2013 Apr;36(4):368-73. doi: 10.1038/hr.2012.196. Epub 2012 Dec 13. Hypertens Res. 2013. PMID: 23235712 Review.
Cited by
-
The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) and arthritic diseases: therapeutic potential for RAS inhibitors.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Aug 12. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01890-z. Online ahead of print. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40796991 Review.
-
Protective role of Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharides against chondrocyte extracellular matrix degeneration through lncRNA GAS5 in osteoarthritis.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Jun 22;24(2):532. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11459. eCollection 2022 Aug. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35837034 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying obesity in degenerative spine and joint diseases.Bone Res. 2024 Dec 11;12(1):71. doi: 10.1038/s41413-024-00388-8. Bone Res. 2024. PMID: 39658574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of SOX family transcription factors in osteoarthritis.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2457520. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2457520. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 39887675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The non-linear relationships between fat mass and lean body mass with arthritis.Lipids Health Dis. 2025 Apr 1;24(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02525-6. Lipids Health Dis. 2025. PMID: 40170043 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

