Biopolymer-Based Filtration Materials
- PMID: 34056334
- PMCID: PMC8153993
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c00791
Biopolymer-Based Filtration Materials
Abstract
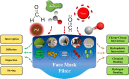
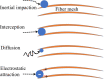
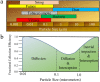
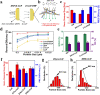
Biobased materials such as cellulose, chitin, silk, soy, and keratin are attractive alternatives to conventional synthetic materials for filtration applications. They are cheap, naturally abundant, and easily fabricated with tunable surface chemistry and functionality. With the planet's increasing crisis due to pollution, the need for proper filtration of air and water is undeniably urgent. Additionally, fibers that are antibacterial and antiviral are critical for public health and in medical environments. The current COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the necessity for cheap, easily mass-produced antiviral fiber materials. Biopolymers can fill these roles very well by utilizing their intrinsic material properties, surface chemistry, and hierarchical fiber morphologies for efficient and eco-friendly filtration of physical, chemical, and biological pollutants. Further, they are biodegradable, making them attractive as sustainable, biocompatible green filters. This review presents various biopolymeric materials generated from proteins and polysaccharides, their synthesis and fabrication methods, and notable uses in filtration applications.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Liu J.; Dunne F. O.; Fan X.; Fu X.; Zhong W.-H. A protein-functionalized microfiber/protein nanofiber Bi-layered air filter with synergistically enhanced filtration performance by a viable method. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 229, 115837.10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115837. - DOI
-
- Ki C. S.; Gang E. H.; Um I. C.; Park Y. H. Nanofibrous membrane of wool keratose/silk fibroin blend for heavy metal ion adsorption. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 302 (1), 20–26. 10.1016/j.memsci.2007.06.003. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

