Electrospun Chitosan-based Fibers for Wound Healing Applications
- PMID: 34056619
- PMCID: PMC8159176
Electrospun Chitosan-based Fibers for Wound Healing Applications
Abstract
Chitosan, a natural-occurring biopolymer, is biocompatible to tissues with excellent antibacterial and hemostatic properties, which makes it a great candidate among wound dressing materials. In this paper, electrospun fiber-based wound dressings from blend chitosan and/or polyethylene oxide (PEO) and/or polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fibers were reviewed. The incorporation of these water-soluble copolymers allows the entanglement of the rigid chitosan molecular chains during electrospinning leading to the production of continuous nonwoven fibers having average diameters ranging from several tenths to hundredths of nanometers. Increasing chitosan composition in the fibers improves the bulk mechanical strength of the fiber mats due to the rigid molecular structure of chitosan. The nano-sized pores within the fiber mats promote permeability of the fiber dressings, which further enhances the exchange of oxygen and nutrients with outside environment. In addition, the porous fiber mat structure facilitates the absorption of wound exudates while reducing the possibility of bacterial infections. Several studies in antibacterial and anti-inflammatory responses of chitosan-based electrospun fibers were discussed in this short review. More importantly, inclusions of small molecule drugs and/or biological agents are possible in chitosan-based electrospun fibers, which provide a multi-purpose treatment capability for wound healing applications.
Keywords: Chitosan; Drug Delivery; Electrospinning; Fibers; Wound Healing.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
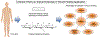
Similar articles
-
Wound dressing based on electrospun PVA/chitosan/starch nanofibrous mats: Fabrication, antibacterial and cytocompatibility evaluation and in vitro healing assay.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Feb 1;122:238-254. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.115. Epub 2018 Oct 18. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 30342125
-
Incorporation of metal-organic frameworks into electrospun chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) nanofibrous membrane with enhanced antibacterial activity for wound dressing application.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Apr 27;158:9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.116. Online ahead of print. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32353508
-
Electrospun PVA nanofiber mat for topical Deflazacort delivery: accentuated anti-inflammatory efficacy for wound healing.Pharm Dev Technol. 2023 Nov;28(9):884-895. doi: 10.1080/10837450.2023.2270057. Epub 2023 Nov 15. Pharm Dev Technol. 2023. PMID: 37830868
-
Metal nanoparticles incorporated chitosan-based electrospun nanofibre mats for wound dressing applications: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Dec;282(Pt 6):137352. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.137352. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39522916 Review.
-
State-of-the-Art Review of Electrospun Gelatin-Based Nanofiber Dressings for Wound Healing Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Feb 25;12(5):784. doi: 10.3390/nano12050784. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35269272 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Polymer Concentration on the Release Rates of Proteins from Single- and Double-Network Hydrogels.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 30;24(23):16970. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316970. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069293 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Magnesium-Phosphate Particle Incorporation into Co-Electrospun Chitosan-Elastin Membranes for Skin Wound Healing.Mar Drugs. 2022 Sep 29;20(10):615. doi: 10.3390/md20100615. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36286439 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan-Based Composites: Development and Perspective in Food Preservation and Biomedical Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Jul 25;15(15):3150. doi: 10.3390/polym15153150. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37571044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome and Secretome Analysis of Staphylotrichum longicolleum DSM105789 Cultured on Agro-Residual and Chitinous Biomass.Microorganisms. 2021 Jul 25;9(8):1581. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9081581. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34442660 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of wound dressing based on the combination of silver@curcumin nanoparticles and electrospun chitosan nanofibers on wound healing.Bioengineered. 2022 Feb;13(2):4328-4339. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2031415. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35137655 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chou S-F, Lai J-Y, Cho C-H, Lee C-H, Relationships between surface roughness/stiffness of chitosan coatings and fabrication of corneal keratocyte spheroids: Effect of degree of deacetylation, Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces. 142 (2016) 105–113. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.02.051. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
