Unsulfated biotechnological chondroitin by itself as well as in combination with high molecular weight hyaluronan improves the inflammation profile in osteoarthritis in vitro model
- PMID: 34056757
- PMCID: PMC8453819
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.29907
Unsulfated biotechnological chondroitin by itself as well as in combination with high molecular weight hyaluronan improves the inflammation profile in osteoarthritis in vitro model
Abstract
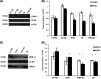
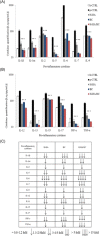
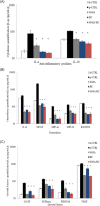
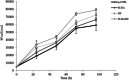
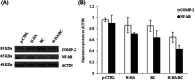
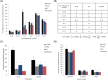
Several studies suggest that inflammation has a pivotal role during the progression of osteoarthritis (OA) and cytokines have been identified as the main process mediators. This study aimed to explore the ability to modulate the main OA pro-inflammatory biomarkers of novel gels (H-HA/BC) based on high molecular weight hyaluronan (H-HA) and unsulfated biotechnological chondroitin (BC). For the first time, BC was tested also in combination with H-HA on human primary cells isolated from pathological knee joints. Specifically, the experiments were performed using an OA in vitro model based on human chondrocytes and synoviocytes. To evaluate the anti-inflammatory effects of H-HA/BC in comparison with H-HA and BC single gels, NF-kB, COMP-2, MyD88, MMP-13 and a wide range of cytokines, known to be specific biomarkers in OA (e.g., IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α), were evaluated. In addition, cell morphology and proliferation occurring in the presence of either H-HA/BC or single components were assessed using time-lapse video microscopy. It was shown that synovial fluids and cells isolated from OA suffering patients, presented a cytokine pattern respondent to an ongoing inflammation status. H-HA and BC significantly reduced the levels of 23 biomarkers associated with cartilage damage. However, H-HA/BC decreased significantly 24 biological mediators and downregulated 19 of them more efficiently than the single components. In synoviocytes cultures, cytokine analyses proved that H-HA/BC gels re-established an extracellular environment more similar to a healthy condition reducing considerably the concentration of 11 analytes. Instead, H-HA and BC significantly modulated 7 (5 only with a longer treatment) and 8 biological cytokines, respectively. Our results suggest that H-HA/BC beyond the viscosupplementation effect typical for HA-based gels, can improve the inflammation status in joints and thus could be introduced as a valid protective and anti-inflammatory intraarticular device in the field of Class III medical devices for OA treatments.
Keywords: biotechnological chondroitin; human articular chondrocytes; human synoviocytes; hybrid cooperative complexes; inflammation; osteoarthritis.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures


References
-
- Hochberg MC, Altman RD, April KT, et al. American College of Rheumatology 2012 recommendations for the use of non pharmacologic and pharmacologic therapies in osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012;4:465‐474. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

