Structure-based design and characterization of novel fusion-inhibitory lipopeptides against SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variants
- PMID: 34057039
- PMCID: PMC8216258
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2021.1937329
Structure-based design and characterization of novel fusion-inhibitory lipopeptides against SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variants
Abstract
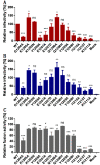
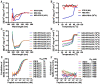
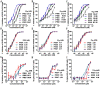
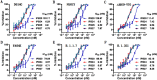
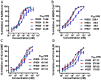
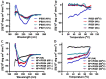
The ongoing pandemic of COVID-19, caused by SARS-CoV-2, has severely impacted the global public health and socio-economic stability, calling for effective vaccines and therapeutics. In this study, we continued our efforts to develop more efficient SARS-CoV-2 fusion inhibitors and achieved significant findings. First, we found that the membrane-proximal external region (MPER) sequence of SARS-CoV-2 spike fusion protein plays a critical role in viral infectivity and can serve as an ideal template for design of fusion-inhibitory peptides. Second, a panel of novel lipopeptides was generated with greatly improved activity in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 fusion and infection. Third, we showed that the new inhibitors maintained the potent inhibitory activity against emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants, including those with the major mutations of the B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 strains circulating in the United Kingdom and South Africa, respectively. Fourth, the new inhibitors also cross-inhibited other human CoVs, including SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, HCoV-229E, and HCoV-NL63. Fifth, the structural properties of the new inhibitors were characterized by circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy and crystallographic approach, which revealed the mechanisms underlying the high binding and inhibition. Combined, our studies provide important information for understanding the mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 fusion and a framework for the development of peptide therapeutics for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 and other CoVs.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; fusion inhibitor; lipopeptide; membrane fusion; spike protein.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

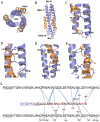
Similar articles
-
Design of Potent Membrane Fusion Inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2, an Emerging Coronavirus with High Fusogenic Activity.J Virol. 2020 Jul 1;94(14):e00635-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00635-20. Print 2020 Jul 1. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32376627 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 (previously 2019-nCoV) infection by a highly potent pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitor targeting its spike protein that harbors a high capacity to mediate membrane fusion.Cell Res. 2020 Apr;30(4):343-355. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0305-x. Epub 2020 Mar 30. Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32231345 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing the solubility of SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors to increase future prospects for clinical development.J Virol. 2025 Mar 18;99(3):e0215924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02159-24. Epub 2025 Feb 4. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 39902960 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of S-protein RBD and hACE2 Interaction for Control of SARSCoV- 2 Infection (COVID-19).Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021;21(6):689-703. doi: 10.2174/1389557520666201117111259. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33208074 Review.
-
Priming of SARS-CoV-2 S protein by several membrane-bound serine proteinases could explain enhanced viral infectivity and systemic COVID-19 infection.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100135. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.015980. Epub 2020 Dec 6. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33268377 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A pan-coronavirus peptide inhibitor prevents SARS-CoV-2 infection in mice by intranasal delivery.Sci China Life Sci. 2023 Oct;66(10):2201-2213. doi: 10.1007/s11427-023-2410-5. Epub 2023 Aug 11. Sci China Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37574525
-
Significance of Conserved Regions in Coronavirus Spike Protein for Developing a Novel Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Feb 24;11(3):545. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11030545. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36992129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dimerized fusion inhibitor peptides targeting the HR1-HR2 interaction of SARS-CoV-2.RSC Adv. 2023 Mar 20;13(13):8779-8793. doi: 10.1039/d2ra07356k. eCollection 2023 Mar 14. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 36950081 Free PMC article.
-
Design of a bifunctional pan-sarbecovirus entry inhibitor targeting the cell receptor and viral fusion protein.J Virol. 2023 Aug 31;97(8):e0019223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00192-23. Epub 2023 Aug 14. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37578234 Free PMC article.
-
Potent inhibition of diverse Omicron sublineages by SARS-CoV-2 fusion-inhibitory lipopeptides.Antiviral Res. 2022 Dec;208:105445. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105445. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Antiviral Res. 2022. PMID: 36265805 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
