TIP30 overcomes gefitinib resistance by regulating cytoplasmic and nuclear EGFR signaling in non-small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 34058054
- PMCID: PMC8486181
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.15000
TIP30 overcomes gefitinib resistance by regulating cytoplasmic and nuclear EGFR signaling in non-small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
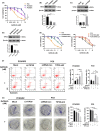
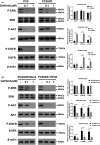
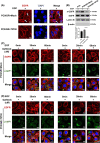
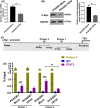
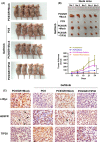
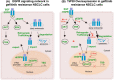
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) (eg, gefitinib) exert potent therapeutic efficacy in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring EGFR-activating mutations. However, the resistance to EGFR TKIs limits their clinical therapeutic efficacy. TIP30, a newly identified tumor suppressor, appears to be involved in the regulation of cytoplasmic and nuclear EGFR signaling in NSCLC. Our previous study demonstrated that TIP30 regulated EGF-dependent cyclin D1 transcription in human lung adenocarcinoma and suppressed tumorigenesis. In the present study, the involvement of TIP30 in combating gefitinib resistance in NSCLC was determined for the first time in vitro and in vivo. Gain and loss of function studies showed that overexpression of TIP30 effectively sensitized cells to gefitinib in vitro, whereas TIP30 inhibition promoted gefitinib cell resistance. Moreover, TIP30 negatively regulated the activation of the p-AKT and p-MEK signaling pathways in PC9/GR. Importantly, PC9/GR harbored high levels of nuclear EGFR, and overexpression of TIP30 restored irregular EGFR trafficking and degradation from early endosomes to the late endosomes, decreasing the nuclear accumulation of EGFR, which may partly or totally inhibit EGFR-mediated induction of c-Myc transcription. Xenographic tumors induced by overexpression of TIP30 by PC9/GR cells in nude mice were suppressed compared with their original counterparts. Overall, it was revealed that TIP30 overexpression restored gefitinib sensitivity in NSCLC cells and attenuated the cytoplasmic and nuclear EGFR signaling pathways and may be a promising biomarker in gefitinib resistance in NSCLC.
Keywords: EGFR; TIP30; gefitinib resistance; non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cucurbitacin B Induces the Lysosomal Degradation of EGFR and Suppresses the CIP2A/PP2A/Akt Signaling Axis in Gefitinib-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Molecules. 2019 Feb 12;24(3):647. doi: 10.3390/molecules24030647. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30759826 Free PMC article.
-
244-MPT overcomes gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 29;6(42):44274-88. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6236. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26517520 Free PMC article.
-
TIP30 loss enhances cytoplasmic and nuclear EGFR signaling and promotes lung adenocarcinogenesis in mice.Oncogene. 2013 May 2;32(18):2273-81, 2281e.1-12. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.253. Epub 2012 Jun 25. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 22733137 Free PMC article.
-
An update of the mechanisms of resistance to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in breast cancer: Gefitinib (Iressa) -induced changes in the expression and nucleo-cytoplasmic trafficking of HER-ligands (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2007 Jul;20(1):3-10. Int J Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 17549382 Review.
-
Cell Behavior of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Is at EGFR and MicroRNAs Hands.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 19;22(22):12496. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212496. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830377 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in the role of membrane-bound transcription factors in carcinogenesis and therapy.Discov Oncol. 2024 Oct 15;15(1):559. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01414-1. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39404930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in malignant tumors: molecular mechanisms and future perspective.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Sep 17;7(1):329. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01168-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 36115852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide association study of the age of onset of type 1 diabetes reveals HTATIP2 as a novel T cell regulator.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 1;14:1101488. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1101488. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36817429 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic silencing of HTATIP2 in glioblastoma contributes to treatment resistance by enhancing nuclear translocation of the DNA repair protein MPG.Mol Oncol. 2023 Sep;17(9):1744-1762. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13494. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Mol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37491696 Free PMC article.
-
EGFR trafficking: effect of dimerization, dynamics, and mutation.Front Oncol. 2023 Sep 11;13:1258371. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1258371. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37752992 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Roskoski R Jr. Small molecule inhibitors targeting the EGFR/ErbB family of protein‐tyrosine kinases in human cancers. Pharmacol Res. 2019;139:395‐411. Epub 2018/12/01. - PubMed
-
- Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first‐line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation‐positive non‐small‐cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG‐0802): a multicentre, open‐label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12(8):735‐742. Epub 2011/07/26. - PubMed
-
- Kazandjian D, Blumenthal GM, Yuan W, He K, Keegan P, Pazdur R. FDA approval of gefitinib for the treatment of patients with metastatic EGFR mutation‐positive non‐small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22(6):1307‐1312. Epub 2016/03/17. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

