On-field evaluation of a ultra-rapid fluorescence immunoassay as a frontline test for SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic
- PMID: 34058287
- PMCID: PMC8161776
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2021.114201
On-field evaluation of a ultra-rapid fluorescence immunoassay as a frontline test for SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic
Abstract
Background: Viral RNA amplification by real-time RT-PCR still represents the gold standard for the detection of SARS-CoV-2, but the development of rapid, reliable and easy-to-perform diagnostic methods is crucial for public health, because of the need of shortening the time of result-reporting with a cost-efficient approach.
Objectives: The aim of our research was to assess the performance of FREND™ COVID-19 Ag assay (NanoEntek, South Korea) as a ultra-rapid frontline test for SARS-CoV-2 identification, in comparison with RT-PCR and another COVID-19 antigen fluorescence immunoassay (FIA).
Study design: The qualitative FIA FREND™ test, designed to detect within 3 min the Nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2, was evaluated using nasopharyngeal swabs in Universal Transport Medium (UTM™, Copan Diagnostics Inc, US) from suspected COVID-19 cases who accessed the Emergency Room of the Ospedale Policlinico San Martino, Genoa, Liguria, Northwest Italy. Diagnostic accuracy was determined in comparison with SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR and STANDARD F™ COVID-19 Ag FIA test (SD BIOSENSOR Inc., Republic of Korea).
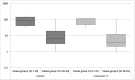
Results: In November 2020, 110 nasopharyngeal samples were collected consecutively; 60 resulted RT-PCR positive. With respect to RT-PCR results, sensitivity and specificity of FREND™ COVID-19 Ag test were 93.3 % (95 % CI: 83.8-98.2) and 100 % (95 % CI: 92.9-100), respectively. FREND™and STANDARD F™ COVID-19 Ag FIA assays showed a concordance of 96.4 % (Cohen's k = 0.93, 95 % CI: 0.86-0.99).
Conclusions: FREND™ FIA test showed high sensitivity and specificity in nasopharyngeal swabs. The assay has the potential to become an important tool for an ultra-rapid identification of SARS-CoV-2 infection, particularly in situations with limited access to molecular diagnostics.
Keywords: COVID-19 identification; Fluorescence immunoassay (FIA); Rapid antigen diagnostic test; SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- OMS Laboratory testing strategy recommendations for COVID-19. Interim Guidance. 2020;21(March)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

