Hypoxia-induced lncHILAR promotes renal cancer metastasis via ceRNA for the miR-613/206/ 1-1-3p/Jagged-1/Notch/CXCR4 signaling pathway
- PMID: 34058384
- PMCID: PMC8531137
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.05.020
Hypoxia-induced lncHILAR promotes renal cancer metastasis via ceRNA for the miR-613/206/ 1-1-3p/Jagged-1/Notch/CXCR4 signaling pathway
Retraction in
-
Retraction Notice to: Hypoxia-induced lncHILAR promotes renal cancer metastasis via ceRNA for the miR-613/206/ 1-1-3p/Jagged-1/Notch/CXCR4 signaling pathway.Mol Ther. 2025 Mar 5;33(3):1303. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2025.01.044. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Mol Ther. 2025. PMID: 39892388 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
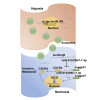
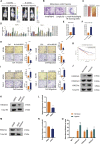
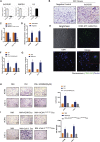
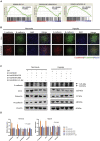
Hypoxia has been identified as a common contributor to tumor progression, including invasion and metastasis. However, the underlying mechanisms of enhanced invasion and metastasis under hypoxia remain unclear. A hypoxic microenvironment promotes invasion and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) by upregulating expression of LOC100506178, which we named hypoxia-induced long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) associated with RCC (lncHILAR). Knockdown of lncHILAR inhibited cell invasion and migration, whereas overexpression of lncHILAR, conversely, facilitated cell invasion and migration of RCC cells. Notably, hypoxic RCC cells secreted exosomes packaged with lncHILAR, which were taken up by normoxic RCC cells and then drove normoxic cell invasion. Mechanistically, lncHILAR elevated RCC invasion and metastasis by acting as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) for miR-613/206/1-1-3p, which led to the upregulation of Jagged-1 and the C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4). Activation of the Jagged-1/Notch/CXCR4 axis induced RCC metastasis. lncHILAR promotes RCC cell invasion and metastasis via ceRNA for the miR-613/206/1-1-3p/Jagged-1/Notch/CXCR4 axis. The novel lncHILAR may thus serve as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target in RCC.
Keywords: RCC; exosomes; hypoxia; lncRNA; metastasis.
Copyright © 2021 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Bray F., Ferlay J., Soerjomataram I., Siegel R.L., Torre L.A., Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Khanna A., Crane A., Yerram N., Sun D., Ericson K., Lundy S.D., Abouassaly R. Contemporary management of advanced renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2018;16:438–446. - PubMed
-
- Schito L., Semenza G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factors: master regulators of cancer progression. Trends Cancer. 2016;2:758–770. - PubMed
-
- Deng S.J., Chen H.Y., Ye Z., Deng S.C., Zhu S., Zeng Z., He C., Liu M.L., Huang K., Zhong J.X. Hypoxia-induced LncRNA-BX111 promotes metastasis and progression of pancreatic cancer through regulating ZEB1 transcription. Oncogene. 2018;37:5811–5828. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

