Psychiatric Comorbidities Are Highly Prevalent in Nonesophageal Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Diseases
- PMID: 34058413
- PMCID: PMC8627515
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.05.044
Psychiatric Comorbidities Are Highly Prevalent in Nonesophageal Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Diseases
Abstract
Background & aims: The prevalence of psychiatric comorbidity in nonesophageal eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGIDs) has not been studied. We aimed to ascertain the prevalence of psychiatric diagnoses and psychiatric medication use in children, adolescents, and adults with EGIDs and to assess whether psychiatric comorbidity affects clinical presentation.
Methods: This was a retrospective cohort study of newly diagnosed patients with a nonesophageal EGID at the University of North Carolina from 2008 to 2020. Psychiatric diagnoses and medications were extracted from medical records. We compared the clinical and demographic features of EGID patients with and without psychiatric diagnoses.
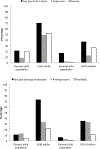
Results: Of 79 patients (mean 23.3 years of age, 53% male, 78% White) with a nonesophageal EGID diagnosis, 40 (51%) were diagnosed with a comorbid psychiatric disease. Anxiety (37%) and depression (28%) were most common. There were also 40 (51%) patients treated medically for a psychiatric diagnosis. Patients with a psychiatric diagnosis were more commonly ≥18 years of age at the time of EGID diagnosis (odds ratio [OR], 3.95, 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.20-13.02) and had endorsed symptoms of nausea (OR, 5.31; 95% CI, 1.33-21.22) and dysphagia (OR, 4.24; 95% CI, 1.18-15.26).
Conclusion: Psychiatric diagnoses were very common in nonesophageal EGID patients with approximately 7 in 10 adults and one-third of children diagnosed. Similar proportions were found for psychiatric medication use. We also found that psychiatric illness may influence age of clinical presentation and symptoms. Providers should assess for concomitant psychiatric comorbidities in EGID patients.
Keywords: Comorbidity; Eosinophilic Esophagitis; Gastrointestinal Disease; Psychiatric.
Copyright © 2022 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Natural History of Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Diseases Is Influenced by Age of Onset and Location of Involvement.Am J Gastroenterol. 2024 Sep 1;119(9):1813-1820. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002869. Epub 2024 May 16. Am J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38752626 Free PMC article.
-
Increased prevalence of autonomic dysfunction due to postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome in patients with eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders.J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2019 Mar;28(1):47-51. doi: 10.15403/jgld.2014.1121.281.syd. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2019. PMID: 30851172
-
Disease Course and Treatment Response of Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Diseases in Children With Liver Transplantation: Long-Term Follow-Up.Am J Gastroenterol. 2021 Jan 1;116(1):188-197. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000934. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33065587
-
Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disorders.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019 Oct;57(2):272-285. doi: 10.1007/s12016-019-08732-1. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30903439 Review.
-
Epidemiology of Nonesophageal Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Diseases in Symptomatic Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020 Jun;8(6):1994-2003.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.01.060. Epub 2020 Feb 28. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020. PMID: 32061717
Cited by
-
Segmental overlap is common in eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases and impacts clinical presentation and treatment.Dis Esophagus. 2025 Jan 7;38(1):doaf011. doi: 10.1093/dote/doaf011. Dis Esophagus. 2025. PMID: 40036388 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between anxiety and decreased quality of life in patients with non-esophageal eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases.JGH Open. 2023 Dec 23;8(1):e13025. doi: 10.1002/jgh3.13025. eCollection 2024 Jan. JGH Open. 2023. PMID: 38268958 Free PMC article.
-
Global trends in research related to functional dyspepsia and anxiety or depression over the past two decades: a bibliometric analysis.Front Neurosci. 2023 Nov 2;17:1218001. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1218001. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38027507 Free PMC article.
-
The Natural History of Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Diseases Is Influenced by Age of Onset and Location of Involvement.Am J Gastroenterol. 2024 Sep 1;119(9):1813-1820. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002869. Epub 2024 May 16. Am J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38752626 Free PMC article.
-
Impressions and aspirations from the FDA GREAT VI Workshop on Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disorders Beyond Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Perspectives for Progress in the Field.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022 Mar;149(3):844-853. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2021.12.768. Epub 2021 Dec 22. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34953790 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Walker MM, Potter M, Talley NJ. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis and other eosinophilic gut diseases distal to the oesophagus. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018;4(4):271–280. - PubMed
-
- Gonsalves N Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disorders. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 2019;57(2):272–285. - PubMed
-
- Egan M, Furuta GT. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases beyond eosinophilic esophagitis. Ann Allergy, Asthma Immunol 2018;121(2):162–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

