Extracellular CIRP decreases Siglec-G expression on B-1a cells skewing them towards a pro-inflammatory phenotype in sepsis
- PMID: 34058975
- PMCID: PMC8165807
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-021-00318-y
Extracellular CIRP decreases Siglec-G expression on B-1a cells skewing them towards a pro-inflammatory phenotype in sepsis
Abstract
Background: Sepsis is a life-threatening disease syndrome caused by a dysregulated host response to infection and injury. Extracellular cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (eCIRP) acts as a damage-associated molecular pattern. Peritoneal cavity (PerC) B-1a cells attenuate inflammation and tissue injury by spontaneous releasing natural IgM and IL-10. Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-type lectin-G (Siglec-G) is a CD33-related receptor highly expressed in B-1a cells to serve critical immunoregulatory functions. In sepsis, B-1a cell numbers in PerC are decreased. We hypothesized that eCIRP causes the reduction of PerC B-1a cells and alters their function during sepsis.
Methods: Sepsis was induced in WT and CIRP-/- mice by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP). PerC washout cells were collected and B-1a cells and Siglec-G were assessed by flow cytometry. Mice were i.p. injected with recombinant murine (rm) CIRP and after 20 h, Siglec-G expression in PerC B-1a cells were assessed. PerC B-1a cells were treated with rmCIRP for 4 h and Siglec-G expression was assessed. PerC B-1a cells were pre-treated with anti-Siglec-G Ab and then after stimulated with rmCIRP for 24 h, IL-6 levels in the culture supernatants were assessed.
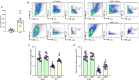
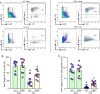
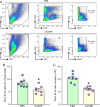
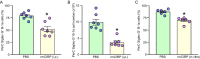
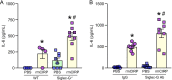
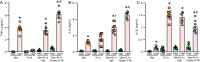
Results: eCIRP levels in the PerC were elevated in septic mice. In WT mice, the frequencies and numbers of total and Siglec-G+ B-1a cells in the PerC were significantly decreased in the CLP group compared to sham group, whereas in CIRP-/- mice, their frequencies and numbers in sepsis were significantly rescued compared to WT septic mice. Mice injected with rmCIRP showed decreased frequencies and numbers of total and Siglec-G+ PerC B-1a cells compared to PBS-injected mice. In vitro treatment of PerC B-1a cells with rmCIRP demonstrated significant reduction in Siglec-G mRNA and protein compared to PBS group. PerC B-1a cells treated with anti-Siglec-G Ab had significantly higher production of IL-6 in response to rmCIRP compared to IgG control. Anti-Siglec-G Ab treated B-1a cells co-cultured with macrophages produced significantly higher levels of IL-6, and TNF-α, and lower levels of IL-10 compared to IgG-treated B-1a cells and macrophage co-cultures stimulated with rmCIRP.
Conclusion: eCIRP reduces PerC B-1a cell pool and skews them to a pro-inflammatory phenotype by downregulating Siglec-G expression. Targeting eCIRP will retain Siglec-G expressing B-1a cells in the PerC and preserve their anti-inflammatory function in sepsis.
Keywords: B-1a cells; Sepsis; Siglec-G; TLR4; eCIRP.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest in this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Frontline Science: Extracellular CIRP generates a proinflammatory Ly6G+ CD11bhi subset of low-density neutrophils in sepsis.J Leukoc Biol. 2021 Jun;109(6):1019-1032. doi: 10.1002/JLB.3HI0620-416R. Epub 2020 Oct 18. J Leukoc Biol. 2021. PMID: 33070370 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular CIRP promotes Kupffer cell inflammatory polarization in sepsis.Front Immunol. 2024 May 30;15:1411930. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1411930. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38881891 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Siglec-G on Immune Cells in Sepsis.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 23;12:621627. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.621627. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33708213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular CIRP Promotes GPX4-Mediated Ferroptosis in Sepsis.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 29;13:903859. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.903859. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35844517 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular CIRP (eCIRP) and inflammation.J Leukoc Biol. 2019 Jul;106(1):133-146. doi: 10.1002/JLB.3MIR1118-443R. Epub 2019 Jan 15. J Leukoc Biol. 2019. PMID: 30645013 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Forgotten Brother: The Innate-like B1 Cell in Multiple Sclerosis.Biomedicines. 2022 Mar 4;10(3):606. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10030606. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35327408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging roles and therapeutic potential of B cells in sepsis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 8;13:1034667. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1034667. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36425582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular CIRP Upregulates Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression via the NF-kappaB and ERK1/2 Signaling Pathways in Psoriatic Keratinocytes.Mediators Inflamm. 2022 Sep 6;2022:5978271. doi: 10.1155/2022/5978271. eCollection 2022. Mediators Inflamm. 2022. PMID: 36110097 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Cold-Inducible RNA-Binding Protein: Progress from Discovery to Present.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 9;26(8):3524. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083524. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophils disrupt B-1a cell homeostasis by targeting Siglec-G to exacerbate sepsis.Cell Mol Immunol. 2024 Jul;21(7):707-722. doi: 10.1038/s41423-024-01165-7. Epub 2024 May 24. Cell Mol Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38789529 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

