Identification of the prognostic value of ferroptosis-related gene signature in breast cancer patients
- PMID: 34059009
- PMCID: PMC8165796
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08341-2
Identification of the prognostic value of ferroptosis-related gene signature in breast cancer patients
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer (BRCA) is a malignant tumor with high morbidity and mortality, which is a threat to women's health worldwide. Ferroptosis is closely related to the occurrence and development of breast cancer. Here, we aimed to establish a ferroptosis-related prognostic gene signature for predicting patients' survival.
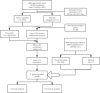
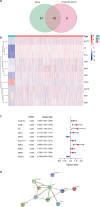
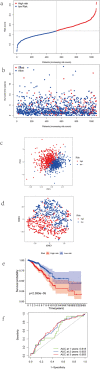
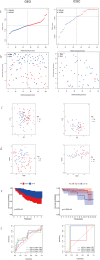
Methods: Gene expression profile and corresponding clinical information of patients from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. The Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO)-penalized Cox regression analysis model was utilized to construct a multigene signature. The Kaplan-Meier (K-M) and Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves were plotted to validate the predictive effect of the prognostic signature. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes, Genomes (KEGG) pathway and single-sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA) were performed for patients between the high-risk and low-risk groups divided by the median value of risk score.
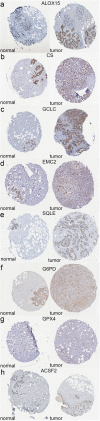
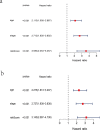
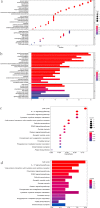
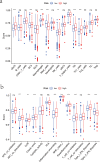
Results: We constructed a prognostic signature consisted of nine ferroptosis-related genes (ALOX15, CISD1, CS, GCLC, GPX4, SLC7A11, EMC2, G6PD and ACSF2). The Kaplan-Meier curves validated the fine predictive accuracy of the prognostic signature (p < 0.001). The area under the curve (AUC) of the ROC curves manifested that the ferroptosis-related signature had moderate predictive power. GO and KEGG functional analysis revealed that immune-related responses were largely enriched, and immune cells, including activated dendritic cells (aDCs), dendritic cells (DCs), T-helper 1 (Th1), were higher in high-risk groups (p < 0.001). Oppositely, type I IFN response and type II IFN response were lower in high-risk groups (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Our study indicated that the ferroptosis-related prognostic signature gene could serve as a novel biomarker for predicting breast cancer patients' prognosis. Furthermore, we found that immunotherapy might play a vital role in therapeutic schedule based on the level and difference of immune-related cells and pathways in different risk groups for breast cancer patients.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Ferroptosis; Immune status; Prognostic signature.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors state that there are no potential competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Construction and analysis of a novel ferroptosis-related gene signature predicting prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma.FEBS Open Bio. 2021 Nov;11(11):3005-3018. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13288. Epub 2021 Oct 16. FEBS Open Bio. 2021. PMID: 34499810 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a novel ferroptosis-related gene signature for predicting prognosis and immune microenvironment in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Sep;98:107789. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107789. Epub 2021 Jun 12. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34130150
-
A ferroptosis-related gene signature predicts overall survival in patients with lung adenocarcinoma.Future Oncol. 2021 Apr;17(12):1533-1544. doi: 10.2217/fon-2020-1113. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Future Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33432837
-
A Novel Pancreatic Cancer Hypoxia Status Related Gene Signature for Prognosis and Therapeutic Responses.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Jul;66(7):1684-1703. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00807-x. Epub 2023 Jul 5. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37405638 Review.
-
Ferroptosis-related NFE2L2 and NOX4 Genes are Potential Risk Prognostic Biomarkers and Correlated with Immunogenic Features in Glioma.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2023 Mar;81(1):7-17. doi: 10.1007/s12013-022-01124-x. Epub 2023 Jan 11. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2023. PMID: 36627482 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Risk-Scoring Model Based on Evaluation of Ferroptosis-Related Genes in Osteosarcoma.J Oncol. 2022 Mar 28;2022:4221756. doi: 10.1155/2022/4221756. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35386212 Free PMC article.
-
A novel disulfidptosis-associated expression pattern in breast cancer based on machine learning.Front Genet. 2023 Jun 29;14:1193944. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1193944. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37456667 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and evaluation of a multifactorial clinical model for discriminating benign and malignant breast tumors using LASSO algorithm based on retrospective cohort study.Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Dec 15;14(12):5628-5643. doi: 10.62347/ILIJ7959. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39803643 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Learning Identify Ferroptosis-Related Genes as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241272036. doi: 10.1177/15330338241272036. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 39169865 Free PMC article.
-
Intersection of ferroptosis and nanomaterials brings benefits to breast cancer.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025 Jul 22;41(1):119. doi: 10.1007/s10565-025-10067-x. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40691737 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

