Luteolin transforms the polarity of bone marrow-derived macrophages to regulate the cytokine storm
- PMID: 34059076
- PMCID: PMC8165957
- DOI: 10.1186/s12950-021-00285-5
Luteolin transforms the polarity of bone marrow-derived macrophages to regulate the cytokine storm
Abstract
Background: Macrophages are indispensable regulators of inflammatory responses. Macrophage polarisation and their secreted inflammatory factors have an association with the outcome of inflammation. Luteolin, a flavonoid abundant in plants, has anti-inflammatory activity, but whether luteolin can manipulate M1/M2 polarisation of bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) to suppress inflammation is still unclear. This study aimed to observe the effects of luteolin on the polarity of BMDMs derived from C57BL/6 mice and the expression of inflammatory factors, to explore the mechanism by which luteolin regulates the BMDM polarity.
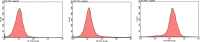
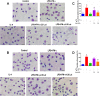
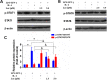
Methods: M1-polarised BMDMs were induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) + interferon (IFN)-γ and M2-polarisation were stimulated with interleukin (IL)-4. BMDM morphology and phagocytosis were observed by laser confocal microscopy; levels of BMDM differentiation and cluster of differentiation (CD)11c or CD206 on the membrane surface were assessed by flow cytometry (FCM); mRNA and protein levels of M1/M2-type inflammatory factors were performed by qPCR and ELISA, respectively; and the expression of p-STAT1 and p-STAT6 protein pathways was detected by Western-blotting.
Results: The isolated mouse bone marrow cells were successfully differentiated into BMDMs, LPS + IFN-γ induced BMDM M1-phenotype polarisation, and IL-4 induced M2-phenotype polarisation. After M1-polarised BMDMs were treated with luteolin, the phagocytosis of M1-polarized BMDMs was reduced, and the M1-type pro-inflammatory factors including IL-6, tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and CD86 were downregulated while the M2-type anti-inflammatory factors including IL-10, IL-13, found in inflammatory zone (FIZZ)1, Arginase (Arg)1 and CD206 were upregulated. Additionally, the expression of M1-type surface marker CD11c decreased. Nevertheless, the M2-type marker CD206 increased; and the levels of inflammatory signalling proteins phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription (p-STAT)1 and p-STAT6 were attenuated and enhanced, respectively.
Conclusions: Our study suggests that luteolin may transform BMDM polarity through p-STAT1/6 to regulate the expression of inflammatory mediators, thereby inhibiting inflammation. Naturally occurring luteolin holds promise as an anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory agent.
Keywords: Bone marrow-derived macrophage polarisation; Cytokines; Inflammation; Luteolin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

