MAPK14 over-expression is a transcriptomic feature of polycythemia vera and correlates with adverse clinical outcomes
- PMID: 34059095
- PMCID: PMC8166116
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-021-02913-3
MAPK14 over-expression is a transcriptomic feature of polycythemia vera and correlates with adverse clinical outcomes
Abstract
Background: The transcriptomic signature has not been fully elucidated in PV, as well as mRNA markers for clinical variables (thrombosis, leukemic transformation, survival, etc.). We attempted to reveal and validate crucial co-expression modules and marker mRNAs correlating with polycythemia vera (PV) by weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA).
Material and methods: The GSE57793/26014/61629 datasets were downloaded from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database and integrated into one fused dataset. By R software and 'WGCNA' package, the PV-specific co-expression module was identified, the pathway enrichment profile of which was obtained by over-representation analysis (ORA). Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network and hub gene analysis identified MAPK14 as our target gene. Then the distribution of MAPK14 expression in different disease/mutation types, were depicted based on external independent datasets. Genome-scale correlation analysis revealed the association of MAPK14 and JAK/STAT family genes. Then gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was performed to detect the activated and suppressed pathways associating with MAPK14 expression. Moreover, GSE47018 dataset was utilized to compare clinical variables (thrombosis, leukemic transformation, survival, etc.) between MAPK14-high and MAPK14-low groups.
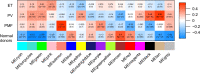
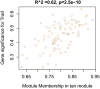
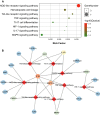
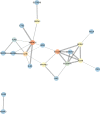
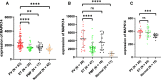
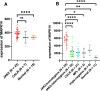
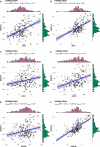
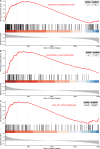
Results: An integrated dataset including 177 samples (83 PV, 35 ET, 17 PMF and 42 normal donors) were inputted into WGCNA. The 'tan' module was identified as the PV-specific module (R2 = 0.56, p = 8e-16), the genes of which were dominantly enriched in pro-inflammatory pathways (Toll-like receptor (TLR)/TNF signaling, etc.). MAPK14 is identified as the top hub gene in PV-related PPI network with the highest betweenness. External datasets validated that the MAPK14 expression was significantly higher in PV than that of essential thrombocytosis (ET)/primary myelofibrosis (PMF) patients and normal donors. JAK2 homozygous mutation carriers have higher level of MAPK14 than that of other mutation types. The expression of JAK/STAT family genes significantly correlated with MAPK14, which also contributed to the activation of oxidated phosphorylation, interferon-alpha (IFNα) response and PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling, etc. Moreover, MAPK14-high group have more adverse clinical outcomes (splenectomy, thrombosis, disease aggressiveness) and inferior survival than MAPK14-low group.
Conclusion: MAPK14 over-expression was identified as a transcriptomic feature of PV, which was also related to inferior clinical outcomes. The results provided novel insights for biomarkers and therapeutic targets for PV.
Keywords: Expression; MAPK14; Polycythemia vera; WGCNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia: 2015 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification and management.Am J Hematol. 2015 Feb;90(2):162-73. doi: 10.1002/ajh.23895. Am J Hematol. 2015. PMID: 25611051 Review.
-
Polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia: 2021 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification and management.Am J Hematol. 2020 Dec;95(12):1599-1613. doi: 10.1002/ajh.26008. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Am J Hematol. 2020. PMID: 32974939 Review.
-
Polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia: 2019 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification and management.Am J Hematol. 2019 Jan;94(1):133-143. doi: 10.1002/ajh.25303. Epub 2018 Nov 9. Am J Hematol. 2019. PMID: 30281843
-
Activated PRKCD-mediated neutrophil extracellular traps pathway may be the prothrombotic mechanism of neutrophils in polycythemia vera patients based on clinical retrospective analysis and bioinformatics study.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Jan 25;127:111366. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111366. Epub 2023 Dec 20. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38128308
-
The role of JAK2 V617F mutation, spontaneous erythropoiesis and megakaryocytopoiesis, hypersensitive platelets, activated leukocytes, and endothelial cells in the etiology of thrombotic manifestations in polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2006 Jun;32(4 Pt 2):381-98. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-942759. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2006. PMID: 16810614 Review.
Cited by
-
Deepening Our Understanding of the Factors Affecting Landscape of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: What Do We Know about Them?Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 20;15(4):1348. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041348. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831689 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zini R, Guglielmelli P, Pietra D, Rumi E, Rossi C, Rontauroli S, Genovese E, Fanelli T, Calabresi L, Bianchi E, et al. CALR mutational status identifies different disease subtypes of essential thrombocythemia showing distinct expression profiles. Blood Cancer J. 2017;7(12):638. doi: 10.1038/s41408-017-0010-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

