Post-Treatment Sevoflurane Protects Against Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in Neonatal Rats by Downregulating Histone Methyltransferase G9a and Upregulating Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 (NRF2)
- PMID: 34059615
- PMCID: PMC8178995
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.930042
Post-Treatment Sevoflurane Protects Against Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in Neonatal Rats by Downregulating Histone Methyltransferase G9a and Upregulating Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 (NRF2)
Abstract
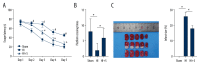
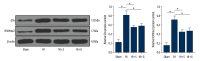
BACKGROUND Perinatal hypoxia and subsequent reduction of cerebral blood flow leads to neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury (HIBI), resulting in severe disability and even death. Preconditioning or post-conditioning with sevoflurane protects against cerebral injury. This study investigated the mechanism of sevoflurane in HIBI. MATERIAL AND METHODS The HIBI model of neonatal rats was established and the model rats were post-treated with sevoflurane. The oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) cell model was established, and the OGD cells were transfected with NRF2-siRNA plasmid and post-treated with sevoflurane. The Morris water maze test was used to detect the motor activity, spatial learning, and memory ability of HIBI rats. Histological stainings were performed to observe the area of cerebral infarction, record the number of neurons in the hippocampus, and assess neuron apoptosis. The levels of inflammatory factors were detected by ELISA. The protein levels of histone methyltransferase G9a and histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2) were detected by western blot assay. The apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry. RESULTS Sevoflurane post-treatment significantly shortened the escape latency of HIBI neonatal rats, increased the density of neurons, reduced the area of cerebral infarction, and decreased the levels of inflammatory factors and neuronal apoptosis. Sevoflurane post-treatment decreased G9a and H3K9me2 levels, and G9a level was negatively correlated with NRF2 level. NRF2 silencing reversed the alleviation of sevoflurane post-treatment on OGD-induced cell injury. CONCLUSIONS Sevoflurane post-treatment promotes NRF2 expression by inhibiting G9a and H3K9me2, thus alleviating HIBI in neonatal rats.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The mechanism of sevoflurane post-treatment alleviating hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy by affecting histone methyltransferase G9a in rats.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):9790-9805. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1995105. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34672892 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Sevoflurane Postconditioning on Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury via Nrf2-Regulated Ferroptosis in Neonatal Rats.Anesth Analg. 2025 Sep 1;141(3):648-659. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000007547. Epub 2025 May 16. Anesth Analg. 2025. PMID: 40378085 Free PMC article.
-
Sevoflurane Post-Conditioning Ameliorates Neuronal Deficits and Axon Demyelination After Neonatal Hypoxic Ischemic Brain Injury: Role of Microglia/Macrophage.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Nov;41(8):1801-1816. doi: 10.1007/s10571-020-00949-5. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 32880098 Free PMC article.
-
New progress of isoflurane, sevoflurane and propofol in hypoxic-ischemic brain injury and related molecular mechanisms based on p75 neurotrophic factor receptor.Ibrain. 2021 Jun 28;7(2):132-140. doi: 10.1002/j.2769-2795.2021.tb00075.x. eCollection 2021 Jun. Ibrain. 2021. PMID: 37786902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mimickers of hypoxic-ischaemic brain injury in term neonates: What the radiologist should know.SA J Radiol. 2024 Feb 29;28(1):2810. doi: 10.4102/sajr.v28i1.2810. eCollection 2024. SA J Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38628264 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
EHMT2 affects microglia polarization and aggravates neuronal damage and inflammatory response via regulating HMOX1.Transl Neurosci. 2023 Jul 27;14(1):20220276. doi: 10.1515/tnsci-2022-0276. eCollection 2023 Jan 1. Transl Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37529171 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism of sevoflurane post-treatment alleviating hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy by affecting histone methyltransferase G9a in rats.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):9790-9805. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1995105. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34672892 Free PMC article.
-
Gelsemine Exerts Neuroprotective Effects on Neonatal Mice with Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury by Suppressing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress via Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2023 May;48(5):1305-1319. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03815-6. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Neurochem Res. 2023. PMID: 36449197
-
Sevoflurane Post-treatment Mitigates Oxygen-glucose Deprivationinduced Pyroptosis of Hippocampal Neurons by Regulating the Mafb/DUSP14 Axis.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2022;19(3):245-254. doi: 10.2174/1567202619666220802104426. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 35927915
-
Comprehensive overview of Nrf2-related epigenetic regulations involved in ischemia-reperfusion injury.Theranostics. 2022 Sep 11;12(15):6626-6645. doi: 10.7150/thno.77243. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 36185600 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xu Y, Xue H, Zhao P, et al. Isoflurane postconditioning induces concentration- and timing-dependent neuroprotection partly mediated by the GluR2 AMPA receptor in neonatal rats after brain hypoxia-ischemia. J Anesth. 2016;30(3):427–36. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

