Efficacy and Safety of Netakimab, A Novel Anti-IL-17 Monoclonal Antibody, in Patients with Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis. Results of A 54-Week Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled PLANETA Clinical Trial
- PMID: 34060012
- PMCID: PMC8322379
- DOI: 10.1007/s13555-021-00554-4
Efficacy and Safety of Netakimab, A Novel Anti-IL-17 Monoclonal Antibody, in Patients with Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis. Results of A 54-Week Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled PLANETA Clinical Trial
Abstract
Introduction: Netakimab (NTK), an original humanized anti-interleukin-17 monoclonal antibody, showed therapeutic efficacy in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis in a phase 2 clinical study. Herein we report the results of 54 weeks of a phase 3 PLANETA trial aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of two NTK regimens vs. placebo.
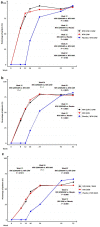
Methods: Two hundred thirteen patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis were randomly assigned to receive NTK 120 mg once every 2 weeks (NTK Q2W), NTK 120 mg once every 4 weeks (NTK Q4W) or placebo. During the first 3 weeks, patients received subcutaneous injections of NTK or placebo (according to the allocation) once a week. Patients in the NTK Q2W group then received NTK at weeks 4, 6, 8 and 10. Subjects in the NTK Q4W group received NTK at weeks 6 and 10 and placebo at weeks 4 and 8. Patients in the placebo group received placebo injections at weeks 4, 6, 8 and 10. Treatment was unblinded at week 12. During the open-label phase, patients in both NTK groups continued to receive NTK Q4W. The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients in each group who achieved a ≥ 75% reduction from baseline in psoriasis area and severity index (PASI 75) at week 12.
Results: A total of 77.7%, 83.3% and 0% of patients had a PASI 75 response at week 12 in the NTK Q2W, NTK Q4W and placebo groups, respectively (P < 0.0001, Fisher's exact test, ITT). The effect was maintained throughout the 1-year treatment. NTK showed a good safety profile and low immunogenicity.
Conclusion: Treatment with NTK results in high rates of sustained clinical response in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. The study is ongoing; thus, long-term use efficacy and safety data are forthcoming.
Clinical trial registration: The trial is registered at the US National Institutes of Health (ClinicalTrials.gov; NCT03390101).
Keywords: Interleukin-17 inhibitors; Netakimab; Psoriasis.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Erdes S, Nasonov E, Kunder E, et al. Primary efficacy of netakimab, a novel interleukin-17 inhibitor, in the treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis in adults. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2020;38(1):27–34. - PubMed
-
- Bakulev AL, Samtsov AV, Kubanov AA, Khairutdinov VR, Kokhan MM, Artemyeva AV, Derbin SI, Chernyaeva EV, Ivanov RA. Long-term efficacy and safety of netakimab in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis. Results of phase II open-label extension clinical study BCD-085–2-ext. Vestnik dermatologii i venerologii. 2019;95(3):54–64. doi: 10.25208/0042-4609-2019-95-3-54-64. - DOI
-
- Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE). https://www.eortc.be/services/doc/ctc/ctcae_4.03_2010-06-14_quickreferen.... Accessed 13 Jan 2021.
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

