Antagonism of Sigma-1 receptor blocks heavy alcohol drinking and associated hyperalgesia in male mice
- PMID: 34060104
- PMCID: PMC8295198
- DOI: 10.1111/acer.14635
Antagonism of Sigma-1 receptor blocks heavy alcohol drinking and associated hyperalgesia in male mice
Abstract
Background: Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is a complex psychiatric disease characterized by high alcohol intake as well as hyperkatifeia and hyperalgesia during withdrawal. A role for Sigma-1 receptors (Sig-1Rs) in the rewarding and reinforcing effects of alcohol has started to emerge in recent years, as rat studies have indicated that Sig-1R hyperactivity may result in excessive alcohol drinking. Sig-1R studies in mice are very scarce, and its potential role in alcohol-induced hyperalgesia is also unknown.
Methods: In this study, we investigated the role of Sig-1R in alcohol drinking and associated hyperalgesia in male mice, using an intermittent access 2-bottle choice model of heavy drinking.
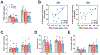
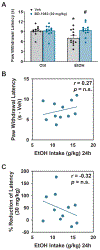
Results: The Sig-1R antagonist BD-1063 was found dose dependently to reduce both alcohol intake and preference, without affecting either water or sucrose intake, suggesting that the effects are specific for alcohol. Notably, the ability of BD-1063 to suppress ethanol intake correlated with the individual baseline levels of alcohol drinking, suggesting that the treatment was more efficacious in heavy drinking animals. In addition, BD-1063 reversed alcohol-induced hyperalgesia during withdrawal, assessed using an automatic Hargreaves test, without affecting thermal sensitivity in alcohol-naïve animals or locomotor activity in either group.
Conclusions: These data show that Sig-1R antagonism dose-dependently reduced ethanol consumption in heavy drinking mice as well as its efficacy in reducing alcohol-induced hyperalgesia. These findings provide a foundation for the development of novel treatments for AUD and associated pain states.
Keywords: addiction; alcoholism; allostasis; dependence; drinking; hyperkatifeia; pain.
© 2021 by the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Figures
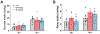
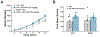
Similar articles
-
Sigma-1 receptor mediates acquisition of alcohol drinking and seeking behavior in alcohol-preferring rats.Behav Brain Res. 2015;287:315-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.03.065. Epub 2015 Apr 4. Behav Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25848705 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol-related behaviors in mice lacking the sigma-1 receptor.Behav Brain Res. 2016 Jan 15;297:196-203. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.10.013. Epub 2015 Oct 14. Behav Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26462569 Free PMC article.
-
The Sigma-2 receptor / transmembrane protein 97 (σ2R/TMEM97) modulator JVW-1034 reduces heavy alcohol drinking and associated pain states in male mice.Neuropharmacology. 2021 Feb 15;184:108409. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108409. Epub 2020 Nov 20. Neuropharmacology. 2021. PMID: 33221481 Free PMC article.
-
Sigma-1 receptor and inflammatory pain.Inflamm Res. 2015 Jun;64(6):377-81. doi: 10.1007/s00011-015-0819-8. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Inflamm Res. 2015. PMID: 25902777 Review.
-
Sigma Receptors and Alcohol Use Disorders.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017;244:219-236. doi: 10.1007/164_2016_97. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28039543 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in drug discovery efforts targeting the sigma 1 receptor system: Implications for novel medications designed to reduce excessive drug and food seeking.Addict Neurosci. 2023 Dec;8:100126. doi: 10.1016/j.addicn.2023.100126. Epub 2023 Aug 27. Addict Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37753198 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitor decreases hyperalgesia in a mouse model of alcohol withdrawal-induced hyperalgesia.Alcohol Clin Exp Res (Hoboken). 2024 Mar;48(3):478-487. doi: 10.1111/acer.15273. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Alcohol Clin Exp Res (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38378262 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Alcohol Drinking Drives Sex-Specific Differences in Affective Behavior and Medial Prefrontal Cortex Activity in CRF1:Cre:tdTomato Transgenic Rats.eNeuro. 2023 Jul 13;10(7):ENEURO.0055-23.2023. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0055-23.2023. Print 2023 Jul. eNeuro. 2023. PMID: 37414553 Free PMC article.
-
Pituitary Adenylate Cyclase-Activating Polypeptide (PACAP) of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis Mediates Heavy Alcohol Drinking in Mice.eNeuro. 2023 Dec 28;10(12):ENEURO.0424-23.2023. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0424-23.2023. Print 2023 Dec. eNeuro. 2023. PMID: 38053471 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in affective states and association with voluntary ethanol intake in Sprague-Dawley rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022 Feb;239(2):589-604. doi: 10.1007/s00213-021-06052-x. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022. PMID: 35044485
References
-
- (2018 NSDUH) 2018 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH), in Series 2018 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH), www.samhsa.gov, pp Table 5.4A—Alcohol Use Disorder in Past Year among Persons Aged 12 or Older, by Age Group and Demographic Characteristics: Numbers in Thousands, 2017 and 2018.
-
- Alonso G, Phan V, Guillemain I, Saunier M, Legrand A, Anoal M, Maurice T (2000) Immunocytochemical localization of the sigma(1) receptor in the adult rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 97:155–170. - PubMed
-
- Aydar E, Palmer CP, Klyachko VA, Jackson MB (2002) The sigma receptor as a ligand-regulated auxiliary potassium channel subunit. Neuron 34:399–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

