A Novel cis Regulatory Element Regulates Human XIST in a CTCF-Dependent Manner
- PMID: 34060915
- PMCID: PMC8300786
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00382-20
A Novel cis Regulatory Element Regulates Human XIST in a CTCF-Dependent Manner
Abstract
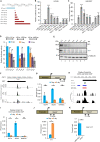
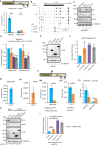
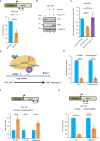
The long noncoding RNA XIST is the master regulator for the process of X chromosome inactivation (XCI) in mammalian females. Here, we report the existence of a hitherto-uncharacterized cis regulatory element (cRE) within the first exon of human XIST, which determines the transcriptional status of XIST during the initiation and maintenance phases of XCI. In the initiation phase, pluripotency factors bind to this cRE and keep XIST repressed. In the maintenance phase of XCI, the cRE is enriched for CTCF, which activates XIST transcription. By employing a CRISPR-dCas9-KRAB-based interference strategy, we demonstrate that binding of CTCF to the newly identified cRE is critical for regulating XIST in a YY1-dependent manner. Collectively, our study uncovers the combinatorial effect of multiple transcriptional regulators influencing XIST expression during the initiation and maintenance phases of XCI.
Keywords: CTCF; XIST; YY1; cis regulatory element; pluripotency factors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Jpx RNA activates Xist by evicting CTCF.Cell. 2013 Jun 20;153(7):1537-51. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.028. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23791181 Free PMC article.
-
A prominent and conserved role for YY1 in Xist transcriptional activation.Nat Commun. 2014 Sep 11;5:4878. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5878. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 25209548 Free PMC article.
-
The pluripotency factor Oct4 interacts with Ctcf and also controls X-chromosome pairing and counting.Nature. 2009 Jul 2;460(7251):128-32. doi: 10.1038/nature08098. Epub 2009 Jun 17. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19536159 Free PMC article.
-
Xist drives spatial compartmentalization of DNA and protein to orchestrate initiation and maintenance of X inactivation.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2020 Jun;64:139-147. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2020.04.009. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32535328 Review.
-
Xist gene regulation at the onset of X inactivation.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2009 Apr;19(2):122-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2009.03.003. Epub 2009 Apr 1. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2009. PMID: 19345091 Review.
Cited by
-
Escaping but not the inactive X-linked protein complex coding genes may achieve X-chromosome dosage compensation and underlie X chromosome inactivation-related diseases.Heliyon. 2023 Jun 27;9(7):e17721. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17721. eCollection 2023 Jul. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37449161 Free PMC article.
-
A de novo YY1 missense variant expanding the Gabriele-de Vries syndrome phenotype and affecting X-chromosome inactivation.Metab Brain Dis. 2022 Oct;37(7):2431-2440. doi: 10.1007/s11011-022-01024-2. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Metab Brain Dis. 2022. PMID: 35829845
-
Multifaceted role of CTCF in X-chromosome inactivation.Chromosoma. 2024 Oct;133(4):217-231. doi: 10.1007/s00412-024-00826-w. Epub 2024 Oct 21. Chromosoma. 2024. PMID: 39433641 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
