Providing Hospitalized Ulcerative Colitis Patients With Practice Guidelines Improves Patient-Reported Outcomes
- PMID: 34061122
- PMCID: PMC8158645
- DOI: 10.1093/jcag/gwaa019
Providing Hospitalized Ulcerative Colitis Patients With Practice Guidelines Improves Patient-Reported Outcomes
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to: Providing Hospitalized Ulcerative Colitis Patients With Practice Guidelines Improves Patient-Reported Outcomes.J Can Assoc Gastroenterol. 2020 Aug 27;4(4):198. doi: 10.1093/jcag/gwaa029. eCollection 2021 Aug. J Can Assoc Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 34337320 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background and aims: Variation in care has been demonstrated among hospitalized patients with ulcerative colitis. Guidelines aim to reduce variation; however, it is known that the uptake of guidelines by physicians is variable. Providing patients with guidelines is a strategy that has not been extensively studied in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Our aim was to evaluate the impact of a patient-directed educational intervention that included treatment guidelines among hospitalized ulcerative colitis patients.
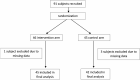
Methods: We performed a quality improvement, cluster-randomized trial at seven tertiary IBD centres. Sites were randomized to implement an educational intervention or standard care for a 6-month period between January 2017 and January 2018. The educational intervention consisted of a patient-directed video that provided a summary of inpatient management guidelines for ulcerative colitis. Primary outcome measures included the length of stay and colectomy at discharge and 6 months. Patient-reported outcomes included trust in physician and patient satisfaction at discharge and at 6 months.
Results: Ninety-one patients were enrolled. No statistically significant differences in length of stay or colectomy were noted. Patients who received the intervention had higher trust in physician as measured by Trust in Physician Score at discharge (69.5 vs. 62.6, P = 0.028) and at 6 months (77.7 vs. 68, P = 0.008). Patient satisfaction as measured by the CACHE questionnaire in the intervention group was higher at discharge (72.8 vs. 67.1, P = 0.04); however, this difference was not sustained.
Conclusion: Empowering patients with guidelines through an educational intervention resulted in differences in trust in physician and patient satisfaction. Further studies are needed for evaluating a strategy of engaging IBD patients to take a more active role in their care. (clinicaltrials.gov, NCT02569333).
Keywords: Compliance/Adherence; Guidelines; Inflammatory bowel disease; Ulcerative colitis.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Canadian Association of Gastroenterology.
References
-
- Reddy SI, Friedman S, Telford JJ, et al. . Are patients with inflammatory bowel disease receiving optimal care? Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;100(6):1357–61. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen GC, Murthy SK, Bressler B, et al. ; CINERGI group . Quality of care and outcomes among hospitalized inflammatory bowel disease patients: A multicenter retrospective study. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2017;23(5):695–701. - PubMed
-
- Lönnfors S, Vermeire S, Greco M, et al. . IBD and health-related quality of life – Discovering the true impact. J Crohns Colitis. 2014;8(10):1281–6. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen GC, Sam J. Rising prevalence of venous thromboembolism and its impact on mortality among hospitalized inflammatory bowel disease patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103(9):2272–80. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical