Ectopic fat in liver and skeletal muscle is associated with shorter overall survival in patients with colorectal liver metastases
- PMID: 34061469
- PMCID: PMC8350209
- DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.12723
Ectopic fat in liver and skeletal muscle is associated with shorter overall survival in patients with colorectal liver metastases
Abstract
Background: Myosteatosis has been associated with shorter overall survival in cancer patients. The increase in ectopic fat might not be limited to skeletal muscle only and might also extend to other sites such as the liver, resulting in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). In this study, we assessed the relationship between myosteatosis and NAFLD and their association with overall survival in patients with colorectal liver metastases undergoing partial hepatectomy.
Methods: Patients were selected from a prospective cohort of 289 consecutive patients with colorectal liver metastases. All patients with a preoperative computed tomography (CT)-scan and liver biopsy obtained during surgery were included. If available a second pre-operative CT scan was used to calculate changes in body composition over time. Muscle radiation attenuation was defined as the average Hounsfield units on CT of all muscle tissue at the L3 level. Liver biopsies were graded by a liver pathologist using the steatosis, activity, and fibrosis scoring system for NAFLD.
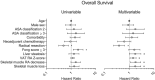
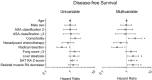
Results: Two-hundred and eighteen patients had an available liver biopsy of which 131 patients had two available pre-operative CT scans with an average time interval of 3.2 months. One-hundred and thirty-five (62%) biopsies were classified as NAFLD. In multivariable Cox-regression analysis, NAFLD [hazard ratio (HR): 1.8, 95%-confidence interval (CI) 1.0-3.0, P = 0.037], increase in myosteatosis (HR 1.8, 95%-CI 1.1-2.9, P = 0.018), and skeletal muscle loss (HR 1.7, 95%-CI 1.0-2.9, P = 0.035) were independently associated with shorter overall survival while high visceral adipose tissue fat content was associated with longer overall survival (HR: 0.7, 95%-CI 0.5-0.9, P = 0.014).
Conclusions: Ectopic fat content of liver as well as skeletal muscle tissue is independently associated with shorter overall survival in patients with colorectal liver metastases, while increased visceral adipose tissue fat content is associated with longer overall survival.
Keywords: Body composition; Colorectal liver metastases; Myosteatosis; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; Sarcopenia; Skeletal muscle loss.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society on Sarcopenia, Cachexia and Wasting Disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
D.D., J.Z., K.K., V.B., C.D., S.R., and S.O.D. declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center M, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- van de Velde CJH. Treatment of liver metastases of colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol 2006;17:727. - PubMed
-
- Weiss L, Grundmann E, Torhorst J, Hartveit F, Moberg I, Eder M, et al. Haematogenous metastatic patterns in colonic carcinoma: an analysis of 1541 necropsies. J Pathol 1986;150:195–203. - PubMed
-
- Rees M, Tekkis PP, Welsh FK, O'Rourke T, John TG. Evaluation of long‐term survival after hepatic resection for metastatic colorectal cancer: a multifactorial model of 929 patients. Ann Surg 2008;247:125–135. - PubMed
-
- de Jong MC, Pulitano C, Ribero D, Strub J, Mentha G, Schulick RD, et al. Rates and patterns of recurrence following curative intent surgery for colorectal liver metastasis: an international multi‐institutional analysis of 1669 patients. Ann Surg 2009;250:440–448. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

