Utilization of Hydrophobic Microenvironment Sensitivity in Diethylpyrocarbonate Labeling for Protein Structure Prediction
- PMID: 34061512
- PMCID: PMC8336574
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c00395
Utilization of Hydrophobic Microenvironment Sensitivity in Diethylpyrocarbonate Labeling for Protein Structure Prediction
Abstract
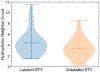
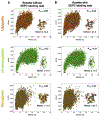
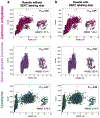
Diethylpyrocarbonate (DEPC) labeling analyzed with mass spectrometry can provide important insights into higher order protein structures. It has been previously shown that neighboring hydrophobic residues promote a local increase in DEPC concentration such that serine, threonine, and tyrosine residues are more likely to be labeled despite low solvent exposure. In this work, we developed a Rosetta algorithm that used the knowledge of labeled and unlabeled serine, threonine, and tyrosine residues and assessed their local hydrophobic environment to improve protein structure prediction. Additionally, DEPC-labeled histidine and lysine residues with higher relative solvent accessible surface area values (i.e., more exposed) were scored favorably. Application of our score term led to reductions of the root-mean-square deviations (RMSDs) of the lowest scoring models. Additionally, models that scored well tended to have lower RMSDs. A detailed tutorial describing our protocol and required command lines is included. Our work demonstrated the considerable potential of DEPC covalent labeling data to be used for accurate higher order structure determination.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Accounting for Neighboring Residue Hydrophobicity in Diethylpyrocarbonate Labeling Mass Spectrometry Improves Rosetta Protein Structure Prediction.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2022 Mar 2;33(3):584-591. doi: 10.1021/jasms.1c00373. Epub 2022 Feb 11. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2022. PMID: 35147431 Free PMC article.
-
Higher-Order Structure Influences the Kinetics of Diethylpyrocarbonate Covalent Labeling of Proteins.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2020 Mar 4;31(3):658-665. doi: 10.1021/jasms.9b00132. Epub 2020 Jan 27. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2020. PMID: 32013423 Free PMC article.
-
Epitope Mapping with Diethylpyrocarbonate Covalent Labeling-Mass Spectrometry.Anal Chem. 2022 Jan 18;94(2):1052-1059. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c04038. Epub 2021 Dec 21. Anal Chem. 2022. PMID: 34932327 Free PMC article.
-
Covalent Labeling with Diethylpyrocarbonate: Sensitive to the Residue Microenvironment, Providing Improved Analysis of Protein Higher Order Structure by Mass Spectrometry.Anal Chem. 2019 Jul 2;91(13):8516-8523. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b01732. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Anal Chem. 2019. PMID: 31150223 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane Protein Binding Interactions Studied in Live Cells via Diethylpyrocarbonate Covalent Labeling Mass Spectrometry.Anal Chem. 2023 May 9;95(18):7178-7185. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c05616. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Anal Chem. 2023. PMID: 37102678 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Workflow for Validating Specific Amino Acid Footprinting Reagents for Protein Higher Order Structure Elucidation.Anal Chem. 2023 Jul 4;95(26):10119-10126. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c01919. Epub 2023 Jun 23. Anal Chem. 2023. PMID: 37351860 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary Structural Information for Antibody-Antigen Complexes from Hydrogen-Deuterium Exchange and Covalent Labeling Mass Spectrometry.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2022 Jul 6;33(7):1303-1314. doi: 10.1021/jasms.2c00108. Epub 2022 Jun 15. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2022. PMID: 35708229 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in mass spectrometry-based footprinting of membrane proteins.Proteomics. 2022 Apr;22(8):e2100222. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202100222. Proteomics. 2022. PMID: 35290716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Energy Resolved Mass Spectrometry Data from Surfaced Induced Dissociation Improves Prediction of Protein Complex Structure.Anal Chem. 2025 Feb 4;97(4):2375-2383. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c05837. Epub 2025 Jan 24. Anal Chem. 2025. PMID: 39854242
-
Predicting ion mobility collision cross sections using projection approximation with ROSIE-PARCS webserver.Brief Bioinform. 2023 Sep 20;24(5):bbad308. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad308. Brief Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 37609950 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Konermann L; Pan J; Liu Y-H, Hydrogen exchange mass spectrometry for studying protein structure and dynamics. Chem. Soc. Rev 2011, 40 (3), 1224–1234. - PubMed
-
- Sinz A, Chemical cross‐linking and mass spectrometry to map three‐dimensional protein structures and protein–protein interactions. Mass Spectrom. Rev 2006, 25 (4), 663–682. - PubMed
-
- Xu G; Chance MR, Hydroxyl radical-mediated modification of proteins as probes for structural proteomics. Chem. Rev 2007, 107 (8), 3514–3543. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

