Cardiovascular complications of COVID-19
- PMID: 34061779
- PMCID: PMC8410051
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.148980
Cardiovascular complications of COVID-19
Abstract
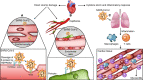
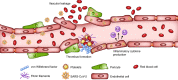
The emergence of the novel SARS coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), has resulted in an unprecedented pandemic that has been accompanied by a global health crisis. Although the lungs are the main organs involved in COVID-19, systemic disease with a wide range of clinical manifestations also develops in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2. One of the major systems affected by this virus is the cardiovascular system. The presence of preexisting cardiovascular disease increases mortality in patients with COVID-19, and cardiovascular injuries, including myocarditis, cardiac rhythm abnormalities, endothelial cell injury, thrombotic events, and myocardial interstitial fibrosis, are observed in some patients with COVID-19. The underlying pathophysiology of COVID-19-associated cardiovascular complications is not fully understood, although direct viral infection of myocardium and cytokine storm have been suggested as possible mechanisms of myocarditis. In this Review, we summarize available data on SARS-CoV-2-related cardiac damage and discuss potential mechanisms of cardiovascular implications of this rapidly spreading virus.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

