The role of AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway in anticancer activity of metformin
- PMID: 34062070
- PMCID: PMC8820546
- DOI: 10.33549/physiolres.934618
The role of AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway in anticancer activity of metformin
Abstract
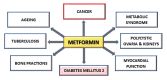
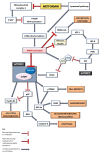
Metformin (MTF) is a widely used drug for the treatment of diabetes mellitus type 2 (DM2) and frequently used as an adjuvant therapy for polycystic ovarian syndrome, metabolic syndrome, and in some cases also tuberculosis. Its protective effect on the cardiovascular system has also been described. Recently, MTF was subjected to various analyzes and studies that showed its beneficial effects in cancer treatment such as reducing cancer cell proliferation, reducing tumor growth, inducing apoptosis, reducing cancer risk in diabetic patients, or reducing likelihood of relapse. One of the MTF's mechanisms of action is the activation of adenosine-monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Several studies have shown that AMPK/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway has anticancer effect in vivo and in vitro. The aim of this review is to present the anticancer activity of MTF highlighting the importance of the AMPK/mTOR pathway in the cancer process.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- CANTORIA MJ, PATEL H, BOROS LG, MEUILLET EJ. Pancreatic cancer-insights into molecular mechanisms and novel approaches to early detection and treatment. London, UK: IntechOpen; 2014. Metformin and pancreatic cancer metabolism. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
