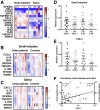
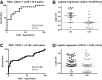
A Novel Noninvasive Method Based on Salivary Inflammatory Biomarkers for the Screening of Celiac Disease
- PMID: 34062280
- PMCID: PMC8531944
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.05.016
A Novel Noninvasive Method Based on Salivary Inflammatory Biomarkers for the Screening of Celiac Disease
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

