Recent Advances in Hepatitis B Treatment
- PMID: 34062711
- PMCID: PMC8147224
- DOI: 10.3390/ph14050417
Recent Advances in Hepatitis B Treatment
Abstract
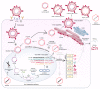
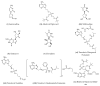
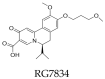
Hepatitis B virus infection affects over 250 million chronic carriers, causing more than 800,000 deaths annually, although a safe and effective vaccine is available. Currently used antiviral agents, pegylated interferon and nucleos(t)ide analogues, have major drawbacks and fail to completely eradicate the virus from infected cells. Thus, achieving a "functional cure" of the infection remains a real challenge. Recent findings concerning the viral replication cycle have led to development of novel therapeutic approaches including viral entry inhibitors, epigenetic control of cccDNA, immune modulators, RNA interference techniques, ribonuclease H inhibitors, and capsid assembly modulators. Promising preclinical results have been obtained, and the leading molecules under development have entered clinical evaluation. This review summarizes the key steps of the HBV life cycle, examines the currently approved anti-HBV drugs, and analyzes novel HBV treatment regimens.
Keywords: HBV; HBV inhibitors; HBV life cycle; HBV treatment; antiviral agents; antiviral therapy; cccDNA; hepatitis B; hepatitis B virus; nucleoside analogues.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
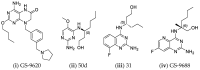
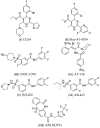
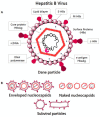
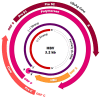
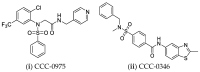
References
-
- World Health Organization Hepatitis B-Key Facts. [(accessed on 14 March 2021)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

