Mutation-Based Antibiotic Resistance Mechanism in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates
- PMID: 34062812
- PMCID: PMC8147353
- DOI: 10.3390/ph14050420
Mutation-Based Antibiotic Resistance Mechanism in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates
Abstract
β-Lactam antibiotics target penicillin-binding proteins and inhibit the synthesis of peptidoglycan, a crucial step in cell wall biosynthesis. Staphylococcus aureus acquires resistance against β-lactam antibiotics by producing a penicillin-binding protein 2a (PBP2a), encoded by the mecA gene. PBP2a participates in peptidoglycan biosynthesis and exhibits a poor affinity towards β-lactam antibiotics. The current study was performed to determine the diversity and the role of missense mutations of PBP2a in the antibiotic resistance mechanism. The methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolates from clinical samples were identified using phenotypic and genotypic techniques. The highest frequency (60%, 18 out of 30) of MRSA was observed in wound specimens. Sequence variation analysis of the mecA gene showed four amino acid substitutions (i.e., E239K, E239R, G246E, and E447K). The E239R mutation was found to be novel. The protein-ligand docking results showed that the E239R mutation in the allosteric site of PBP2a induces conformational changes in the active site and, thus, hinders its interaction with cefoxitin. Therefore, the present report indicates that mutation in the allosteric site of PBP2a provides a more closed active site conformation than wide-type PBP2a and then causes the high-level resistance to cefoxitin.
Keywords: PBP2a; allosteric site; mecA; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; mutation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funding bodies played no role in the design of the study, collection, analysis, or interpretation of the data or in the writing of the manuscript.
Figures
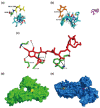
References
-
- Aswani S.A., Abdul-Aziz A. The characterization of mecA gene and SCCmec typing in clinical samples of MRSA. Sci. Lett. 2019;13:1–7.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

