Regulation of Expression of the TIR-Containing Protein C Gene of the Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Strain CFT073
- PMID: 34062817
- PMCID: PMC8147327
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens10050549
Regulation of Expression of the TIR-Containing Protein C Gene of the Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Strain CFT073
Abstract
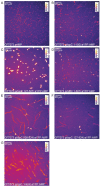
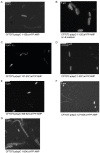
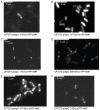
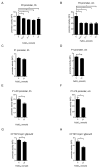
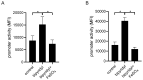
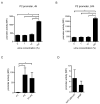
The uropathogenic Escherichia coli strain CFT073 causes kidney abscesses in mice Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-containing protein C (TcpC) dependently and the corresponding gene is present in around 40% of E. coli isolates of pyelonephritis patients. It impairs the Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling chain and the NACHT leucin-rich repeat PYD protein 3 inflammasome (NLRP3) by binding to TLR4 and myeloid differentiation factor 88 as well as to NLRP3 and caspase-1, respectively. Overexpression of the tcpC gene stopped replication of CFT073. Overexpression of several tcpC-truncation constructs revealed a transmembrane region, while its TIR domain induced filamentous bacteria. Based on these observations, we hypothesized that tcpC expression is presumably tightly controlled. We tested two putative promoters designated P1 and P2 located at 5' of the gene c2397 and 5' of the tcpC gene (c2398), respectively, which may form an operon. High pH and increasing glucose concentrations stimulated a P2 reporter construct that was considerably stronger than a P1 reporter construct, while increasing FeSO4 concentrations suppressed their activity. Human urine activated P2, demonstrating that tcpC might be induced in the urinary tract of infected patients. We conclude that P2, consisting of a 240 bp region 5' of the tcpC gene, represents the major regulator of tcpC expression.
Keywords: glucose; hydrogen-Ion concentration; promoter region; uropathogenic Escherichia coli; virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures





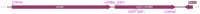
References
-
- Cirl C., Wieser A., Yadav M., Duerr S., Schubert S., Fischer H., Stappert D., Wantia N., Rodriguez N., Wagner H., et al. Subversion of Toll-like receptor signaling by a unique family of bacterial Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-containing proteins. Nat. Med. 2008;14:399–406. doi: 10.1038/nm1734. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Snyder G.A., Cirl C., Jiang J., Chen K., Waldhuber A., Smith P., Römmler F., Snyder N., Fresquez T., Durr S., et al. Molecular mechanisms for the subversion of MyD88 signaling by TcpC from virulent uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2013;110:6985–6990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1215770110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Norenberg D., Wieser A., Magistro G., Hoffmann C., Meyer C., Messerer M., Schubert S. Molecular analysis of a novel Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR)-domain containing virulence protein of Y. pseudotuberculosis among Far East scarlet-like fever serotype I strains. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013;303:583–594. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2013.08.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Salcedo S.P., Marchesini M.I., Lelouard H., Fugier E., Jolly G., Balor S., Muller A., Lapaque N., Demaria O., Alexopoulou L., et al. Brucella control of dendritic cell maturation is dependent on the TIR-containing protein Btp1. PLoS Pathog. 2008;4:e21. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0040021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

