The Cause of Hereditary Hearing Loss in GJB2 Heterozygotes-A Comprehensive Study of the GJB2/DFNB1 Region
- PMID: 34062854
- PMCID: PMC8147375
- DOI: 10.3390/genes12050684
The Cause of Hereditary Hearing Loss in GJB2 Heterozygotes-A Comprehensive Study of the GJB2/DFNB1 Region
Abstract
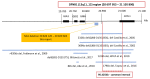
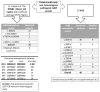
Hearing loss is a genetically heterogeneous sensory defect, and the frequent causes are biallelic pathogenic variants in the GJB2 gene. However, patients carrying only one heterozygous pathogenic (monoallelic) GJB2 variant represent a long-lasting diagnostic problem. Interestingly, previous results showed that individuals with a heterozygous pathogenic GJB2 variant are two times more prevalent among those with hearing loss compared to normal-hearing individuals. This excess among patients led us to hypothesize that there could be another pathogenic variant in the GJB2 region/DFNB1 locus. A hitherto undiscovered variant could, in part, explain the cause of hearing loss in patients and would mean reclassifying them as patients with GJB2 biallelic pathogenic variants. In order to detect an unknown causal variant, we examined 28 patients using NGS with probes that continuously cover the 0.4 Mb in the DFNB1 region. An additional 49 patients were examined by WES to uncover only carriers. We did not reveal a second pathogenic variant in the DFNB1 region. However, in 19% of the WES-examined patients, the cause of hearing loss was found to be in genes other than the GJB2. We present evidence to show that a substantial number of patients are carriers of the GJB2 pathogenic variant, albeit only by chance.
Keywords: DFNB1 region; GJB2 monoallelic variant; hearing loss; next generation sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome Sequencing Unveils the Role of Copy Number Variants in Hearing Loss and Identifies Novel Deletions With Founder Effect in the DFNB1 Locus.Hum Mutat. 2024 Aug 6;2024:9517114. doi: 10.1155/2024/9517114. eCollection 2024. Hum Mutat. 2024. PMID: 40225913 Free PMC article.
-
Hearing Impairment with Monoallelic GJB2 Variants: A GJB2 Cause or Non-GJB2 Cause?J Mol Diagn. 2021 Oct;23(10):1279-1291. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2021.07.007. Epub 2021 Jul 27. J Mol Diagn. 2021. PMID: 34325055
-
Unraveling of Enigmatic Hearing-Impaired GJB2 Single Heterozygotes by Massive Parallel Sequencing: DFNB1 or Not?Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Apr;95(14):e3029. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003029. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27057829 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of Hereditary Hearing Loss in the Middle East: A Systematic Review of the Carrier Frequency of the GJB2 Mutation (35delG).Audiol Neurootol. 2019;24(4):161-165. doi: 10.1159/000502201. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Audiol Neurootol. 2019. PMID: 31487726
-
Systematic Review of Pathogenic GJB2 Variants in the Latino Population.Otol Neurotol. 2020 Feb;41(2):e182-e191. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000002505. Otol Neurotol. 2020. PMID: 31834214
Cited by
-
Genetic screening of a Chinese cohort of children with hearing loss using a next-generation sequencing panel.Hum Genomics. 2023 Jan 4;17(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s40246-022-00449-1. Hum Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36597107 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Genome Sequencing Improves the Diagnosis of DFNB1 Monoallelic Patients.Genes (Basel). 2021 Aug 19;12(8):1267. doi: 10.3390/genes12081267. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34440441 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of GJB2 Gene Mutations in 1330 Deafness Cases of Major Ethnic Groups in Northwest China.Inquiry. 2022 Jan-Dec;59:469580211055571. doi: 10.1177/00469580211055571. Inquiry. 2022. PMID: 35212567 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting Genetic Epidemiology with a Refined Targeted Gene Panel for Hereditary Hearing Impairment in the Taiwanese Population.Genes (Basel). 2023 Apr 7;14(4):880. doi: 10.3390/genes14040880. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107638 Free PMC article.
-
3D Chromatin Organization Involving MEIS1 Factor in the cis-Regulatory Landscape of GJB2.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 23;23(13):6964. doi: 10.3390/ijms23136964. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35805969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shearer A.E., Hildebrand M.S., Smith R.J.H. Hereditary Hearing Loss and Deafness Overview. In: Adam M.P., Ardinger H.H., Pagon R.A., Wallace S.E., Bean L.J.H., Stephens K., Amemiya A., editors. GeneReviews®. University of Washington; Seattle, WA, USA: 1993.
-
- Seeman P., Malikova M., Raskova D., Bendova O., Groh D., Kubalkova M., Sakmaryova I., Seemanova E., Kabelka Z. Spectrum and frequencies of mutations in the GJB2 (Cx26) gene among 156 Czech patients with pre-lingual deafness. Clin. Genet. 2004;66:152–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2004.00283.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

