Cherbonolides M and N from a Formosan Soft Coral Sarcophyton cherbonnieri
- PMID: 34062855
- PMCID: PMC8170881
- DOI: 10.3390/md19050260
Cherbonolides M and N from a Formosan Soft Coral Sarcophyton cherbonnieri
Abstract
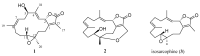
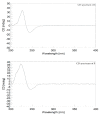
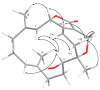
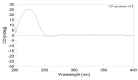
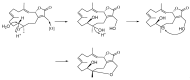
Two new isosarcophine derivatives, cherbonolides M (1) and N (2), were further isolated from a Formosan soft coral Sarcophyton cherbonnieri. The planar structure and relative configuration of both compounds were established by the detailed analysis of the IR, MS, and 1D and 2D NMR data. Further, the absolute configuration of both compounds was determined by the comparison of CD spectra with that of isosarcophine (3). Notably, cherbonolide N (2) possesses the unique cembranoidal scaffold of tetrahydrooxepane with the 12,17-ether linkage fusing with a γ-lactone. In addition, the assay for cytotoxicity of both new compounds revealed that they showed to be noncytotoxic toward the proliferation of A549, DLD-1, and HuCCT-1 cell lines. Moreover, the anti-inflammatory activities of both metabolites were carried out by measuring the N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine/cytochalasin B (fMLF/CB)-induced generation of superoxide anion and elastase release in the primary human neutrophils. Cherbonolide N (2) was found to reduce the generation of superoxide anion (20.6 ± 6.8%) and the elastase release (30.1 ± 3.3%) in the fMLF/CB-induced human neutrophils at a concentration of 30 μM.
Keywords: Sarcophyton cherbonnieri; anti-inflammatory activity; cytotoxicity; isosarcophine derivatives; tetrahydrooxepane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
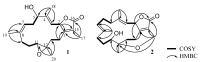
Similar articles
-
New Cembranoids and a Biscembranoid Peroxide from the Soft Coral Sarcophyton cherbonnieri.Mar Drugs. 2018 Aug 6;16(8):276. doi: 10.3390/md16080276. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30082637 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Cembranoids from a Formosa Soft Coral Sarcophyton cherbonnieri.Mar Drugs. 2020 Nov 19;18(11):573. doi: 10.3390/md18110573. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 33228224 Free PMC article.
-
Eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the Formosan soft coral Klyxum molle with inhibitory activity on superoxide generation and elastase release by neutrophils.J Nat Prod. 2013 Sep 27;76(9):1661-7. doi: 10.1021/np400372v. Epub 2013 Sep 10. J Nat Prod. 2013. PMID: 24020806
-
Tortuosenes A and B, new diterpenoid metabolites from the Formosan soft coral Sarcophyton tortuosum.Org Lett. 2014 Mar 7;16(5):1314-7. doi: 10.1021/ol403723b. Epub 2014 Feb 13. Org Lett. 2014. PMID: 24524352
-
Krempfielins N-P, New anti-inflammatory eunicellins from a Taiwanese soft coral Cladiella krempfi.Mar Drugs. 2014 Feb 21;12(2):1148-56. doi: 10.3390/md12021148. Mar Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24566263 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cembranolides and Related Constituents from the Soft Coral Sarcophyton cinereum.Molecules. 2022 Mar 8;27(6):1760. doi: 10.3390/molecules27061760. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35335127 Free PMC article.
-
The application and sustainable development of coral in traditional medicine and its chemical composition, pharmacology, toxicology, and clinical research.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 3;14:1230608. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1230608. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38235111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computationally Assisted Structural Elucidation of Cembranoids from the Soft Coral Sarcophyton tortuosum.Mar Drugs. 2022 Apr 27;20(5):297. doi: 10.3390/md20050297. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35621948 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elkhawas Y.A., Elissawy A.M., Elnaggar M.S., Mostafa N.M., Al-Sayed E., Bishr M.M., Singab A.N.B., Salama O.M. Chemical diversity in species belonging to soft coral genus Sacrophyton and its impact on biological activity: A review. Mar. Drugs. 2020;18:41. doi: 10.3390/md18010041. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

