Hippocampal Subregion and Gene Detection in Alzheimer's Disease Based on Genetic Clustering Random Forest
- PMID: 34062866
- PMCID: PMC8147351
- DOI: 10.3390/genes12050683
Hippocampal Subregion and Gene Detection in Alzheimer's Disease Based on Genetic Clustering Random Forest
Abstract
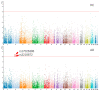
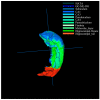
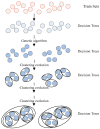
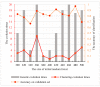
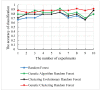
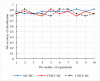
The distinguishable subregions that compose the hippocampus are differently involved in functions associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Thus, the identification of hippocampal subregions and genes that classify AD and healthy control (HC) groups with high accuracy is meaningful. In this study, by jointly analyzing the multimodal data, we propose a novel method to construct fusion features and a classification method based on the random forest for identifying the important features. Specifically, we construct the fusion features using the gene sequence and subregions correlation to reduce the diversity in same group. Moreover, samples and features are selected randomly to construct a random forest, and genetic algorithm and clustering evolutionary are used to amplify the difference in initial decision trees and evolve the trees. The features in resulting decision trees that reach the peak classification are the important "subregion gene pairs". The findings verify that our method outperforms well in classification performance and generalization. Particularly, we identified some significant subregions and genes, such as hippocampus amygdala transition area (HATA), fimbria, parasubiculum and genes included RYR3 and PRKCE. These discoveries provide some new candidate genes for AD and demonstrate the contribution of hippocampal subregions and genes to AD.
Keywords: clustering evolution; genetic algorithm; hippocampus; random forest; subregion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Iglesias J.E., Augustinack J.C., Nguyen K., Player C.M., Player A., Wright M., Roy N., Frosch M.P., Mckee A.C., Wald L.L. A computational atlas of the hippocampal formation using ex vivo, ultra-high resolution mri: Application to adaptive segmentation of in vivo mri. Neuroimage. 2015;115:117–137. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.04.042. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cong S., Risacher S.L., West J.D., Wu Y.C., Apostolova L.G., Tallman E., Rizkalla M., Salama P., Saykin A.J., Shen L. Volumetric Comparison of Hippocampal Subfields Extracted from 4-Minute Accelerated versus 8-Minute High-resolution T2-weighted 3T MRI Scans. Brain Imaging Behav. 2018;12:1583–1595. doi: 10.1007/s11682-017-9819-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

