Pure Ion Chromatograms Combined with Advanced Machine Learning Methods Improve Accuracy of Discriminant Models in LC-MS-Based Untargeted Metabolomics
- PMID: 34063107
- PMCID: PMC8125400
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26092715
Pure Ion Chromatograms Combined with Advanced Machine Learning Methods Improve Accuracy of Discriminant Models in LC-MS-Based Untargeted Metabolomics
Abstract
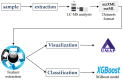
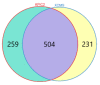
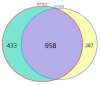
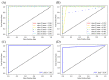
Untargeted metabolomics based on liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (LC-MS) can detect thousands of features in samples and produce highly complex datasets. The accurate extraction of meaningful features and the building of discriminant models are two crucial steps in the data analysis pipeline of untargeted metabolomics. In this study, pure ion chromatograms were extracted from a liquor dataset and left-sided colon cancer (LCC) dataset by K-means-clustering-based Pure Ion Chromatogram extraction method version 2.0 (KPIC2). Then, the nonlinear low-dimensional embedding by uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) showed the separation of samples from different groups in reduced dimensions. The discriminant models were established by extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) based on the features extracted by KPIC2. Results showed that features extracted by KPIC2 achieved 100% classification accuracy on the test sets of the liquor dataset and the LCC dataset, which demonstrated the rationality of the XGBoost model based on KPIC2 compared with the results of XCMS (92% and 96% for liquor and LCC datasets respectively). Finally, XGBoost can achieve better performance than the linear method and traditional nonlinear modeling methods on these datasets. UMAP and XGBoost are integrated into KPIC2 package to extend its performance in complex situations, which are not only able to effectively process nonlinear dataset but also can greatly improve the accuracy of data analysis in non-target metabolomics.
Keywords: KPIC2; LC–MS; Pure Ion Chromatogram; UMAP; XGBoost.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
KPIC2: An Effective Framework for Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Using Pure Ion Chromatograms.Anal Chem. 2017 Jul 18;89(14):7631-7640. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01547. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Anal Chem. 2017. PMID: 28621925
-
Highly automatic and universal approach for pure ion chromatogram construction from liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry data using deep learning.J Chromatogr A. 2023 Aug 30;1705:464172. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2023.464172. Epub 2023 Jun 19. J Chromatogr A. 2023. PMID: 37392637
-
Automated optimization of XCMS parameters for improved peak picking of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry data using the coefficient of variation and parameter sweeping for untargeted metabolomics.Drug Test Anal. 2019 Jun;11(6):752-761. doi: 10.1002/dta.2552. Epub 2018 Dec 25. Drug Test Anal. 2019. PMID: 30479047
-
Advancing untargeted metabolomics using data-independent acquisition mass spectrometry technology.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019 Jul;411(19):4349-4357. doi: 10.1007/s00216-019-01709-1. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019. PMID: 30847570 Review.
-
Integration of GC-MS and LC-MS for untargeted metabolomics profiling.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020 Oct 25;190:113509. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2020.113509. Epub 2020 Aug 2. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020. PMID: 32814263 Review.
Cited by
-
Statistical analysis of feature-based molecular networking results from non-targeted metabolomics data.Nat Protoc. 2025 Jan;20(1):92-162. doi: 10.1038/s41596-024-01046-3. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Nat Protoc. 2025. PMID: 39304763
-
Novel research and future prospects of artificial intelligence in cancer diagnosis and treatment.J Hematol Oncol. 2023 Nov 27;16(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01514-5. J Hematol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38012673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-omic profiling of sarcopenia identifies disrupted branched-chain amino acid catabolism as a causal mechanism and therapeutic target.Nat Aging. 2025 Mar;5(3):419-436. doi: 10.1038/s43587-024-00797-8. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Nat Aging. 2025. PMID: 39910243
References
-
- Musilová J., Glatz Z. Metabolomics-Basic concepts, Strategies and Methodologies. Chemické Listy. 2011;105:745–751.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

