Many Distinct Ways Lead to Drug Resistance in BRAF- and NRAS-Mutated Melanomas
- PMID: 34063141
- PMCID: PMC8148104
- DOI: 10.3390/life11050424
Many Distinct Ways Lead to Drug Resistance in BRAF- and NRAS-Mutated Melanomas
Abstract
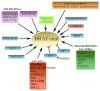
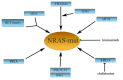
Advanced melanoma is a relentless tumor with a high metastatic potential. The combat of melanoma by using the targeted therapy is impeded because several major driver mutations fuel its growth (predominantly BRAF and NRAS). Both these mutated oncogenes strongly activate the MAPK (MEK/ERK) pathway. Therefore, specific inhibitors of these oncoproteins or MAPK pathway components or their combination have been used for tumor eradication. After a good initial response, resistant cells develop almost universally and need the drug for further expansion. Multiple mechanisms, sometimes very distant from the MAPK pathway, are responsible for the development of resistance. Here, we review many of the mechanisms causing resistance and leading to the dismal final outcome of mutated BRAF and NRAS therapy. Very heterogeneous events lead to drug resistance. Due to this, each individual mechanism would be in fact needed to be determined for a personalized therapy to treat patients more efficiently and causally according to molecular findings. This procedure is practically impossible in the clinic. Other approaches are therefore needed, such as combined treatment with more drugs simultaneously from the beginning of the therapy. This could eradicate tumor cells more rapidly and greatly diminish the possibility of emerging mechanisms that allow the evolution of drug resistance.
Keywords: BRAF; NRAS; drug resistance; melanoma; phenotype switching.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Characterization of genetic alterations in primary human melanomas carrying BRAF or NRAS mutation].Magy Onkol. 2013 Jun;57(2):96-9. Epub 2013 May 20. Magy Onkol. 2013. PMID: 23795354 Hungarian.
-
New Approaches to Targeted Therapy in Melanoma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 17;15(12):3224. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123224. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling in metastatic melanoma.IUBMB Life. 2013 Sep;65(9):748-58. doi: 10.1002/iub.1193. Epub 2013 Jul 29. IUBMB Life. 2013. PMID: 23893853 Review.
-
ROS production induced by BRAF inhibitor treatment rewires metabolic processes affecting cell growth of melanoma cells.Mol Cancer. 2017 Jun 8;16(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0667-y. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28595656 Free PMC article.
-
Novel mechanisms and therapeutic approaches in melanoma: targeting the MAPK pathway.Discov Med. 2015 Jun;19(107):455-61. Discov Med. 2015. PMID: 26175403 Review.
Cited by
-
The Hedgehog/GLI signaling pathway activates transcription of Slug (Snail2) in melanoma cells.Oncol Rep. 2023 Apr;49(4):75. doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8512. Epub 2023 Mar 3. Oncol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36866769 Free PMC article.
-
Cell hiding in colorectal cancer: correlation with response to chemotherapy in vitro and in vivo.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 20;14(1):28762. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79948-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39567584 Free PMC article.
-
Dihydroartemisinin-driven selective anti-lung cancer proliferation by binding to EGFR and inhibition of NRAS signaling pathway-induced DNA damage.Sci Rep. 2024 May 22;14(1):11704. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62126-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38778121 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Melanoma Progression and Treatment Resistance: Role of Cancer Stem-like Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 22;16(2):470. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020470. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38275910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Basis of BRAF Inhibitor Resistance in Melanoma: A Systematic Review.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Aug 21;18(8):1235. doi: 10.3390/ph18081235. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40872623 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Daud A., Bastian B.C. Beyond BRAF in Melanoma. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012;355:99–117. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous