Targeting RTK-PI3K-mTOR Axis in Gliomas: An Update
- PMID: 34063168
- PMCID: PMC8124221
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22094899
Targeting RTK-PI3K-mTOR Axis in Gliomas: An Update
Abstract
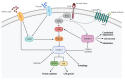
Gliomas are the most common and challenging malignancies of the central nervous system (CNS), due to their infiltrative nature, tendency to recurrence, and poor response to treatments. Indeed, despite the advances in neurosurgical techniques and in radiation therapy, the modest effects of therapy are still challenging. Moreover, tumor recurrence is associated with the onset of therapy resistance; it is therefore critical to identify effective and well-tolerated pharmacological approaches capable of inducing durable responses in the appropriate patient groups. Molecular alterations of the RTK/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway are typical hallmarks of glioma, and several clinical trials targeting one or more players of this axis have been launched, showing disappointing results so far, due to the scarce BBB permeability of certain compounds or to the occurrence of resistance/tolerance mechanisms. However, as RTK/PI3K/mTOR is one of the pivotal pathways regulating cell growth and survival in cancer biology, targeting still remains a strong rationale for developing strategies against gliomas. Future rigorous clinical studies, aimed at addressing the tumor heterogeneity, the interaction with the microenvironment, as well as diverse posology adjustments, are needed-which might unravel the therapeutic efficacy and response prediction of an RTK/PI3K/mTOR-based approach.
Keywords: EGFR; HCGs; PI3K-mTOR; RTKs; glioma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Louis D.N., Perry A., Reifenberger G., von Deimling A., Figarella-Branger D., Cavenee W.K., Ohgaki H., Wiestler O.D., Kleihues P., Ellison D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131:803–820. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human GBM genes and core pathways. Nature. 2008 - PubMed
-
- Zhu H., Acquaviva J., Ramachandran P., Boskovitz A., Woolfenden S., Pfannl R., Bronson R.T., Chen J.W., Weissleder R., Housman D.E., et al. Oncogenic EGFR signaling cooperates with loss of tumor suppressor gene functions in gliomagenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:2712–2716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0813314106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bachoo R.M., Maher E.A., Ligon K.L., Sharpless N.E., Chan S.S., You M.J., Tang Y., DeFrances J., Stover E., Weissleder R., et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor and Ink4a/Arf: Governing terminal differentiation and transformation stem cell to astrocyte axis. Cancer Cell. 2002;1:269–277. doi: 10.1016/S1535-6108(02)00046-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

