Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 34063238
- PMCID: PMC8125096
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13092187
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Prostate Cancer
Abstract
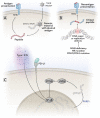
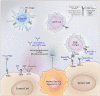
Metastatic prostate cancer is a lethal disease with limited treatment options. Immune checkpoint inhibitors have dramatically changed the treatment landscape of multiple cancer types but have met with limited success in prostate cancer. In this review, we discuss the preclinical studies providing the rationale for the use of immunotherapy in prostate cancer and underlying biological barriers inhibiting their activity. We discuss the predictors of response to immunotherapy in prostate cancer. We summarize studies evaluating immune checkpoint inhibitors either as a single agent or in combination with other checkpoint inhibitors or with other agents such as inhibitors of androgen axis, poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP), radium-223, radiotherapy, cryotherapy, tumor vaccines, chemotherapy, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. We thereafter review future directions including the combination of immune checkpoint blockade with inhibitors of adenosine axis, bispecific T cell engagers, PSMA directed therapies, adoptive T-cell therapy, and multiple other miscellaneous agents.
Keywords: immune checkpoint inhibitors; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
U.S. reports consultancy to Seattle Genetics. N.A. reports consultancy to: Astellas, Astra Zeneca, Aveo, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Calithera, Clovis, Eisai, Eli Lilly, EMD Serono, Exelixis, Foundation Medicine, Genentech, Gilead, Janssen, Merck, MEI Pharma, Nektar, Novartis, Pfizer, Pharmacyclics, and Seattle Genetics. Other authors do not report any COI.
Figures
References
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network Prostate Cancer (Version 2.2021) [(accessed on 23 February 2021)]; Available online: http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/prostate.pdf.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

