Double p52Shc/p46Shc Rat Knockout Demonstrates Severe Gait Abnormalities Accompanied by Dilated Cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 34063460
- PMCID: PMC8155973
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22105237
Double p52Shc/p46Shc Rat Knockout Demonstrates Severe Gait Abnormalities Accompanied by Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
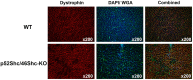
The ubiquitously expressed adaptor protein Shc exists in three isoforms p46Shc, p52Shc, and p66Shc, which execute distinctly different actions in cells. The role of p46Shc is insufficiently studied, and the purpose of this study was to further investigate its functional significance. We developed unique rat mutants lacking p52Shc and p46Shc isoforms (p52Shc/46Shc-KO) and carried out histological analysis of skeletal and cardiac muscle of parental and genetically modified rats with impaired gait. p52Shc/46Shc-KO rats demonstrate severe functional abnormalities associated with impaired gait. Our analysis of p52Shc/46Shc-KO rat axons and myelin sheets in cross-sections of the sciatic nerve revealed the presence of significant anomalies. Based on the lack of skeletal muscle fiber atrophy and the presence of sciatic nerve abnormalities, we suggest that the impaired gait in p52Shc/46Shc-KO rats might be due to the sensory feedback from active muscle to the brain locomotor centers. The lack of dystrophin in some heart muscle fibers reflects damage due to dilated cardiomyopathy. Since rats with only p52Shc knockout do not display the phenotype of p52Shc/p46Shc-KO, abnormal locomotion is likely to be caused by p46Shc deletion. Our data suggest a previously unknown role of 46Shc actions and signaling in regulation of gait.
Keywords: Shc signaling; dystrophin; sciatic nerve.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The p52 isoform of SHC1 is a key driver of breast cancer initiation.Breast Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 15;21(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s13058-019-1155-7. Breast Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31202267 Free PMC article.
-
Opposite effects of the p52shc/p46shc and p66shc splicing isoforms on the EGF receptor-MAP kinase-fos signalling pathway.EMBO J. 1997 Feb 17;16(4):706-16. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.4.706. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9049300 Free PMC article.
-
p66shc negatively regulates insulin-like growth factor I signal transduction via inhibition of p52shc binding to Src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase substrate-1 leading to impaired growth factor receptor-bound protein-2 membrane recruitment.Mol Endocrinol. 2008 Sep;22(9):2162-75. doi: 10.1210/me.2008-0079. Epub 2008 Jul 7. Mol Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18606861 Free PMC article.
-
Src homolog and collagen homolog1 isoforms in acute and chronic liver injuries.Life Sci. 2021 May 15;273:119302. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119302. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33662427 Review.
-
Structure-functional implications of longevity protein p66Shc in health and disease.Ageing Res Rev. 2020 Nov;63:101139. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101139. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Ageing Res Rev. 2020. PMID: 32795504 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in the Production of Genome-Edited Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 25;23(5):2548. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052548. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269691 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Migliaccio E., Mele S., Salcini A.E., Pelicci G., Lai K.V., Superti-Furga G., Pawson T., Di Fiore P.P., Lanfrancone L., Pelicci P.G. Opposite effects of the p52shc/p46shc and p66shc splicing isoforms on the EGF receptor-MAP kinase-fos signalling pathway. EMBO J. 1997;16:706–716. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.4.706. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

