Genome-Wide Identification, Classification and Expression Analysis of the MYB Transcription Factor Family in Petunia
- PMID: 34063617
- PMCID: PMC8124715
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22094838
Genome-Wide Identification, Classification and Expression Analysis of the MYB Transcription Factor Family in Petunia
Abstract
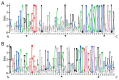
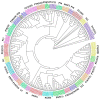
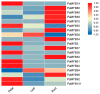
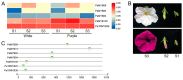
A lot of researches have been focused on the evolution and function of MYB transcription factors (TFs). For revealing the formation of petunia flower color diversity, MYB gene family in petunia was identified and analyzed. In this study, a total of 155 MYB genes, including 40 1R-MYBs, 106 R2R3-MYBs, 7 R1R2R3-MYBs and 2 4R-MYBs, have been identified in the Petunia axillaris genome. Most R2R3 genes contain three exons and two introns, whereas the number of PaMYB introns varies from 0 to 12. The R2R3-MYB members could be divided into 28 subgroups. Analysis of gene structure and protein motifs revealed that members within the same subgroup presented similar exon/intron and motif organization, further supporting the results of phylogenetic analysis. Genes in subgroup 10, 11 and 21 were mainly expressed in petal, not in vegetative tissues. Genes in subgroup 9, 19, 25 and 27 expressed in all tissues, but the expression patterns of each gene were different. According to the promoter analysis, five R2R3-MYB and two MYB-related genes contained MBSI cis-element, which was involved in flavonoid biosynthetic regulation. PaMYB100/DPL has been reported to positively regulate to pigmentation. However, although PaMYB82, PaMYB68 and Pa1RMYB36 contained MBSI cis-element, their function in flavonoid biosynthesis has not been revealed. Consistent with existing knowledge, PaMYBs in subgroup 11 had similar function to AtMYBs in subgroup 6, genes in which played an important role in anthocyanin biosynthesis. In addition, PaMYB1 and PaMYB40 belonged to P9 (S7) and were potentially involved in regulation of flavonoid synthesis in petunia vegetative organs. This work provides a comprehensive understanding of the MYB gene family in petunia and lays a significant foundation for future studies on the function and evolution of MYB genes in petunia.
Keywords: MYB family; Petunia hybrida; anthocyanin biosynthesis; gene expression; transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Members of an R2R3-MYB transcription factor family in Petunia are developmentally and environmentally regulated to control complex floral and vegetative pigmentation patterning.Plant J. 2011 Mar;65(5):771-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04465.x. Epub 2011 Jan 14. Plant J. 2011. PMID: 21235651
-
A novel R2R3-MYB from grape hyacinth, MaMybA, which is different from MaAN2, confers intense and magenta anthocyanin pigmentation in tobacco.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 Sep 9;19(1):390. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1999-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31500571 Free PMC article.
-
Two R2R3-MYB genes, homologs of Petunia AN2, regulate anthocyanin biosyntheses in flower Tepals, tepal spots and leaves of asiatic hybrid lily.Plant Cell Physiol. 2010 Mar;51(3):463-74. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcq011. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20118109
-
Roles of R2R3-MYB transcription factors in transcriptional regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in horticultural plants.Plant Mol Biol. 2018 Sep;98(1-2):1-18. doi: 10.1007/s11103-018-0771-4. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Plant Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30167900 Review.
-
Genome-wide identification of Pistacia R2R3-MYB gene family and function characterization of PcMYB113 during autumn leaf coloration in Pistacia chinensis.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Dec 1;192:16-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.09.092. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34555399 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification, expression analysis of the R2R3-MYB gene family and their potential roles under cold stress in Prunus sibirica.BMC Genomics. 2024 Oct 14;25(1):953. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10868-0. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39402463 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, evolution, and roles of MYB transcription factors proteins in secondary metabolite biosynthetic pathways and abiotic stresses responses in plants: a comprehensive review.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jul 31;16:1626844. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1626844. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40822724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ODORANT1 targets multiple metabolic networks in petunia flowers.Plant J. 2022 Mar;109(5):1134-1151. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15618. Epub 2021 Dec 27. Plant J. 2022. PMID: 34863006 Free PMC article.
-
The R2R3-MYB transcription factor EVER controls the emission of petunia floral volatiles by regulating epicuticular wax biosynthesis in the petal epidermis.Plant Cell. 2023 Dec 21;36(1):174-193. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koad251. Plant Cell. 2023. PMID: 37818992 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of the MYB Gene Family in Cymbidiumensifolium and Its Expression Analysis in Different Flower Colors.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 9;22(24):13245. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413245. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen C., Zhang K., Khurshid M., Li J., He M., Georgiev M.I., Zhang X., Zhou M. MYB Transcription Repressors Regulate Plant Secondary Metabolism. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2019;38:159–170. doi: 10.1080/07352689.2019.1632542. - DOI
-
- Paz-Ares J., Ghosal D., Wienand U., Peterson P.A., Saedler H. The regulatory c1 locus of Zea mays encodes a protein with homology to myb proto-oncogene products and with structural similarities to transcriptional activators. EMBO J. 1987;6:3553–3558. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02684.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

