Sublingual AKBA Exerts Antidepressant Effects in the Aβ-Treated Mouse Model
- PMID: 34063630
- PMCID: PMC8170916
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11050686
Sublingual AKBA Exerts Antidepressant Effects in the Aβ-Treated Mouse Model
Abstract
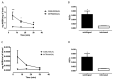
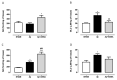
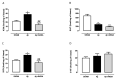
The 3-O-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (AKBA) is the most active compound of Boswellia serrata proposed for treating neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer's disease (AD), characterized in its early phase by alteration in mood. Accordingly, we have previously demonstrated that an intracerebroventricular injection of soluble amyloid beta 1-42 (Aβ) peptide evokes a depressive-like phenotype in rats. We tested the protective effects of AKBA in the mouse model of an Aβ-induced depressive-like phenotype. We evaluated the depressive-like behavior by using the tail suspension test (TST) and the splash test (ST). Behavioral analyses were accompanied by neurochemical quantifications, such as glutamate (GLU), kynurenine (KYN) and monoamines, and by biochemical measurements, such as glial fibrillary acid protein (GFAP), CD11b and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB), in mice prefrontal cortex (PFC) and hippocampus (HIPP). AKBA prevented the depressive-like behaviors induced by Aβ administration, since we recorded a reduction in latency to initiate self-care and total time spent to perform self-care in the ST and reduced time of immobility in the TST. Likewise, the increase in GLU and KYN levels in PFC and HIPP induced by the peptide injection were reverted by AKBA administration, as well as the displayed increase in levels of GFAP and NF-kB in both PFC and HIPP, but not in CD11b. Therefore, AKBA might represent a food supplement suitable as an adjuvant for therapy of depression in early-stage AD.
Keywords: 3-O-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid; beta amyloid; depressive-like behavior; glutamate; kynurenine; sublingual route of administration.
Conflict of interest statement
Bevilacqua is the Health Director of the Pharmaceutica San Marco srl.
Figures

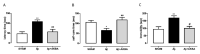

Similar articles
-
3-O-Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid ameliorates chronic unpredictable mild stress induced HPA axis dysregulation in relation with glutamate/GABA aberration in depressive rats.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2021 Dec;48(12):1633-1641. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13567. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34343356
-
Co-administration of 3-Acetyl-11-Keto-Beta-Boswellic Acid Potentiates the Protective Effect of Celecoxib in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Cognitive Impairment in Mice: Possible Implication of Anti-inflammatory and Antiglutamatergic Pathways.J Mol Neurosci. 2016 May;59(1):58-67. doi: 10.1007/s12031-016-0734-7. Epub 2016 Mar 16. J Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26984336
-
Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid ameliorates cognitive deficits and reduces amyloid-β levels in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pathways.Free Radic Biol Med. 2020 Apr;150:96-108. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.02.022. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 32109514
-
The effects of acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid on brain cytokines and memory impairment induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats.Cytokine. 2020 Jul;131:155107. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155107. Epub 2020 May 4. Cytokine. 2020. PMID: 32380425
-
Inhibition of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Exerts Antidepressant-like Effects through Distinct Pathways in Prelimbic and Infralimbic Cortices in Rats under Intracerebroventricular Injection with Streptozotocin.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 8;25(13):7496. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137496. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000602 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Molecular Aspects of Cellular Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease: The Need for a Holistic View of the Early Pathogenesis.Biomolecules. 2021 Dec 1;11(12):1807. doi: 10.3390/biom11121807. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34944450 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Mechanisms of 3-Acetyl-11-keto-β-Boswellic Acid and Piperine in Fluid Percussion Rat Model of Traumatic Brain Injury Targeting Nrf2 and NFkB Signaling.Neurotox Res. 2023 Feb;41(1):57-84. doi: 10.1007/s12640-022-00628-x. Epub 2022 Dec 28. Neurotox Res. 2023. PMID: 36576717
-
Precision Medicine in Alzheimer's Disease: Investigating Comorbid Common Biological Substrates in the Rat Model of Amyloid Beta-Induced Toxicity.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 3;12:799561. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.799561. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35046821 Free PMC article.
-
A Pivotal Role of Nrf2 in Neurodegenerative Disorders: A New Way for Therapeutic Strategies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 May 31;15(6):692. doi: 10.3390/ph15060692. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35745610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Therapeutic Potential of Celastrol in Central Nervous System Disorders: Highlights from In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches.Molecules. 2021 Aug 3;26(15):4700. doi: 10.3390/molecules26154700. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34361850 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ammon H.P. Boswellic Acids and Their Role in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016;928:291–327. - PubMed
-
- Wei C., Fan J., Sun X., Yao J., Guo Y., Zhou B., Shang Y. Acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid ameliorates cognitive deficits and reduces amyloid-beta levels in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pathways. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020;150:96–108. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.02.022. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Haghaei H., Aref Hosseini S.R., Soltani S., Fathi F., Mokhtari F., Karima S., Rashidi M.R. Kinetic and thermodynamic study of beta-Boswellic acid interaction with Tau protein investigated by surface plasmon resonance and molecular modeling methods. Bioimpacts Bi. 2020;10:17–25. doi: 10.15171/bi.2020.03. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

