Stem Cell Therapy for Modulating Neuroinflammation in Neuropathic Pain
- PMID: 34063721
- PMCID: PMC8124149
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22094853
Stem Cell Therapy for Modulating Neuroinflammation in Neuropathic Pain
Abstract
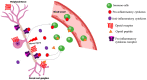
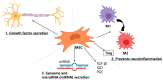
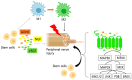
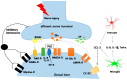
Neuropathic pain (NP) is a complex, debilitating, chronic pain state, heterogeneous in nature and caused by a lesion or disease affecting the somatosensory system. Its pathogenesis involves a wide range of molecular pathways. NP treatment is extremely challenging, due to its complex underlying disease mechanisms. Current pharmacological and nonpharmacological approaches can provide long-lasting pain relief to a limited percentage of patients and lack safe and effective treatment options. Therefore, scientists are focusing on the introduction of novel treatment approaches, such as stem cell therapy. A growing number of reports have highlighted the potential of stem cells for treating NP. In this review, we briefly introduce NP, current pharmacological and nonpharmacological treatments, and preclinical studies of stem cells to treat NP. In addition, we summarize stem cell mechanisms-including neuromodulation in treating NP. Literature searches were conducted using PubMed to provide an overview of the neuroprotective effects of stem cells with particular emphasis on recent translational research regarding stem cell-based treatment of NP, highlighting its potential as a novel therapeutic approach.
Keywords: mesenchymal stem cell; neural stem cell; neuroinflammation; neuromodulation; neuropathic pain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recent Advances in Management of Neuropathic, Nociceptive, and Chronic Pain: A Narrative Review with Focus on Nanomedicine, Gene Therapy, Stem Cell Therapy, and Newer Therapeutic Options.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2024 May;28(5):321-333. doi: 10.1007/s11916-024-01227-5. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2024. PMID: 38386244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review on Stem Cell Therapy for Neuropathic Pain.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;15(4):349-361. doi: 10.2174/1574888X15666200214112908. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32056531
-
Concise review: stem cell therapies for neuropathic pain.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013 May;2(5):394-9. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2012-0122. Epub 2013 Apr 9. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 23572051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adult stem cell as new advanced therapy for experimental neuropathic pain treatment.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:470983. doi: 10.1155/2014/470983. Epub 2014 Aug 13. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25197647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential role of stem cells for neuropathic pain disorders.Neurosurg Focus. 2013 Sep;35(3):E11. doi: 10.3171/2013.6.FOCUS13235. Neurosurg Focus. 2013. PMID: 23991814 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetics of causal relationships between circulating inflammatory proteins and postherpetic neuralgia: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study.Front Neurol. 2024 Jun 21;15:1405694. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1405694. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38974683 Free PMC article.
-
Stem Cell Therapy and Its Significance in Pain Management.Cureus. 2021 Aug 17;13(8):e17258. doi: 10.7759/cureus.17258. eCollection 2021 Aug. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34540482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Management of Neuropathic, Nociceptive, and Chronic Pain: A Narrative Review with Focus on Nanomedicine, Gene Therapy, Stem Cell Therapy, and Newer Therapeutic Options.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2024 May;28(5):321-333. doi: 10.1007/s11916-024-01227-5. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2024. PMID: 38386244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell therapy for neuropathic pain.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Feb 27;16:1119223. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1119223. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36923653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the antinociceptive and reparative actions of mesenchymal stem cells in rats with peripheral neuropathic pain.Ibrain. 2023 Aug 24;9(3):245-257. doi: 10.1002/ibra.12129. eCollection 2023 Fall. Ibrain. 2023. PMID: 37786759 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

