Oligometastatic Cancer: Key Concepts and Research Opportunities for 2021 and Beyond
- PMID: 34063904
- PMCID: PMC8196648
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13112518
Oligometastatic Cancer: Key Concepts and Research Opportunities for 2021 and Beyond
Abstract
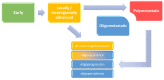
Traditionally, clinicians distinguished three forms of cancer outgrowth [...].
Conflict of interest statement
P.S.: has had in the last three years or has advisory relationships with: Merck-Serono, Servier, and BMS. J.B.V.: has had in the last three years or has consulting/advisory relationships with: Immunomedics, Innate Pharma, Merck-Serono, Merck Sharp & Dome Corp, PCI Biotech, Synthon Biopharmaceuticals, Debiopharm, Cue Biopharma, and WntResearch and received lecture fees from Merck-Serono, MSD, and BMS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modeling growth kinetics and statistical distribution of oligometastases.Semin Radiat Oncol. 2006 Apr;16(2):111-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2005.12.006. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16564446 Review.
-
Oligometastatic breast cancer: where are we now and where are we headed?-a narrative review.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 May;10(5):5954-5968. doi: 10.21037/apm-20-1128. Epub 2020 Sep 10. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 32921069 Review.
-
Radiation for Oligometastatic Lung Cancer in the Era of Immunotherapy: What Do We (Need to) Know?Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 28;13(9):2132. doi: 10.3390/cancers13092132. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33925139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oligometastatic prostate cancer: definitions, clinical outcomes, and treatment considerations.Nat Rev Urol. 2017 Jan;14(1):15-25. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2016.175. Epub 2016 Oct 11. Nat Rev Urol. 2017. PMID: 27725639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery and validation of a serum microRNA signature to characterize oligo- and polymetastatic prostate cancer: not ready for prime time.World J Urol. 2019 Dec;37(12):2557-2564. doi: 10.1007/s00345-018-2609-8. Epub 2018 Dec 21. World J Urol. 2019. PMID: 30578441
Cited by
-
Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Practical Review of Prospective Trials.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 29;14(21):5339. doi: 10.3390/cancers14215339. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essential updates 2021/2022: Surgical outcomes of oligometastasis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2023 Jan 18;7(3):358-366. doi: 10.1002/ags3.12655. eCollection 2023 May. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2023. PMID: 37152775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Patients with Oligometastatic Disease: Clinical State of the Art and Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Feb 23;14(5):1152. doi: 10.3390/cancers14051152. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35267460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging of Oligometastatic Disease.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 10;14(6):1427. doi: 10.3390/cancers14061427. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326586 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amin M.B., Edge S., Greene F., Byrd D.R., Brookland R.K., Washington M.K., Gershenwald J.E., Compton C.C., Hess K.R., Sullivan D.C., et al., editors. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2017.
-
- Lievens Y., Guckenberger M., Gomez D., Hoyer M., Iyengar P., Kindts I., Méndez Romero A., Nevens D., Palma D., Park C., et al. Defining oligometastatic disease from a radiation oncology perspective: An ESTRO-ASTRO consensus document. Radiother. Oncol. 2020;148:157–166. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2020.04.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Guckenberger M., Lievens Y., Bouma A.B., Collette L., Dekker A., deSouza N.M., Dingemans A.C., Fournier B., Hurkmans C., Lecouvet F.E., et al. Characterisation and classification of oligometastatic disease: A European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology and European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer consensus recommendation. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:e18–e28. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30718-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

