Interventions for Nursing Home Residents with Dysphagia-A Scoping Review
- PMID: 34064095
- PMCID: PMC8162353
- DOI: 10.3390/geriatrics6020055
Interventions for Nursing Home Residents with Dysphagia-A Scoping Review
Abstract
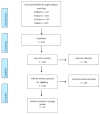
Oropharyngeal dysphagia is common in nursing home residents. The objective of this scoping review was to summarize and disseminate the findings from the literature on interventions for dysphagia in nursing home residents. Searches were conducted in four databases. The criteria for including the studies were nursing home residents, dysphagia, interventions, original research, published in English, Danish, Norwegian, or Swedish with no restriction placed regarding publication date. Excluded were literature reviews, editorial comments, conference abstracts, protocols, papers not available in full text, and studies with a mixed population, for example, geriatric patients and nursing home residents and where the results were not separated between the groups. A total of 14 papers were included and analyzed. The included papers represented interventions focusing on feeding intervention, oral hygiene, caregiver algorithm, stimulation (taste and smell), teaching the residents what to eat, mobilization of the spine, exercises/training, and positioning. This scoping review identifies sparse knowledge about interventions affecting nursing home residents' dysphagia. But the results indicate that multi-component interventions, including staff training, training of residents, and/or next of kin, might be successful. This scoping review clarifies that there is a need for well-designed studies that uncover which specific interventions have an effect in relation to nursing home residents with dysphagia and can serve as a guide for designing multi-component person-centered intervention studies. Future studies should implement high evidence study designs, define the measures of dysphagia, and quantify the severity of dysphagia, its underlying diseases, and comorbidities.
Keywords: care facility; dysphagia; nursing home; nutrition; pneumonia; swallowing disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Baijens L.W., Clave P., Cras P., Ekberg O., Forster A., Kolb G.F., Leners J.C., Masiero S., Mateos-Nozal J., Ortega O., et al. European Society for Swallowing Disorders—European Union Geriatric Medicine Society white paper: Oropharyngeal dysphagia as a geriatric syndrome. Clin. Interv. Aging. 2016;11:1403–1428. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S107750. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wirth R., Dziewas R., Beck A.M., Clave P., Hamdy S., Heppner H.J., Langmore S., Leischker A.H., Martino R., Pluschinski P., et al. Oropharyngeal dysphagia in older persons—From pathophysiology to adequate intervention: A review and summary of an international expert meeting. Clin. Interv. Aging. 2016;11:189–208. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S97481. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

