MMP-9 Deletion Attenuates Arteriovenous Fistula Neointima through Reduced Perioperative Vascular Inflammation
- PMID: 34064140
- PMCID: PMC8196691
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115448
MMP-9 Deletion Attenuates Arteriovenous Fistula Neointima through Reduced Perioperative Vascular Inflammation
Abstract
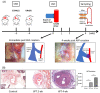
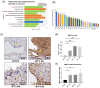
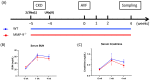
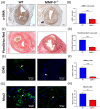
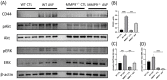
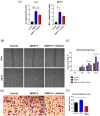
Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) expression is upregulated in vascular inflammation and participates in vascular remodeling, including aneurysm dilatation and arterial neointima development. Neointima at the arteriovenous (AV) fistula anastomosis site primarily causes AV fistula stenosis and failure; however, the effects of MMP-9 on perioperative AV fistula remodeling remain unknown. Therefore, we created AV fistulas (end-to-side anastomosis) in wild-type (WT) and MMP-9 knockout mice with chronic kidney disease to further clarify this. Neointima progressively developed in the AV fistula venous segment of WT mice during the four-week postoperative course, and MMP-9 knockout increased the lumen area and attenuated neointima size by reducing smooth muscle cell and collagen components. Early perioperative AV fistula mRNA sequencing data revealed that inflammation-related gene sets were negatively enriched in AV fistula of MMP-9 knockout mice compared to that in WT mice. qPCR results also showed that inflammatory genes, including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6), intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), were downregulated. In addition, Western blot results showed that MMP-9 knockout reduced CD44 and RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (Akt) and extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) phosphorylation. In vitro, MMP-9 addition enhanced IL-6 and MCP-1 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells, as well as cell migration, which was reversed by an MMP-9 inhibitor. In conclusion, MMP-9 knockout attenuated AV fistula stenosis by reducing perioperative vascular inflammation.
Keywords: arteriovenous fistula; matrix metalloproteinase 9; neointima; vascular inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Oral Charcoal Adsorbents Attenuate Neointima Formation of Arteriovenous Fistulas.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Apr 8;12(4):237. doi: 10.3390/toxins12040237. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32276394 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric oxide prevents aortic neointimal hyperplasia by controlling macrophage polarization.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Aug;34(8):1739-46. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303866. Epub 2014 Jun 12. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24925976
-
Deletion of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 promotes the development of atherosclerosis and arterial neointima formation.Cardiovasc Res. 2014 Feb 1;101(2):236-46. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvt245. Epub 2013 Nov 4. Cardiovasc Res. 2014. PMID: 24193738
-
Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-3 activates MMP-9 mediated vascular smooth muscle cell migration and neointima formation in mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011 Sep;31(9):e35-44. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.225623. Epub 2011 Jun 30. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011. PMID: 21719762
-
Periadventitial Delivery of Simvastatin-Loaded Microparticles Attenuate Venous Neointimal Hyperplasia Associated With Arteriovenous Fistula.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Dec 15;9(24):e018418. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.018418. Epub 2020 Dec 5. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 33283594 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The PPAR-γ Agonist Pioglitazone Modulates Proliferation and Migration in HUVEC, HAOSMC and Human Arteriovenous Fistula-Derived Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 23;24(5):4424. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054424. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901853 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Profile of Cytokines in Arteriovenous Fistula Patients and Their Associations with Maturation Failure.Kidney360. 2022 Jan 13;3(4):677-686. doi: 10.34067/KID.0006022021. eCollection 2022 Apr 28. Kidney360. 2022. PMID: 35721613 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers and the outcomes of ischemic stroke.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Jun 5;16:1171101. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1171101. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37342100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Cardio-Renal Inflammation in Deciding the Fate of the Arteriovenous Fistula in Haemodialysis Therapy.Cells. 2024 Oct 1;13(19):1637. doi: 10.3390/cells13191637. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39404400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Established and emerging techniques for the study of microglia: visualization, depletion, and fate mapping.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Feb 15;18:1317125. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1317125. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38425429 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

