HDAC8 Activates AKT through Upregulating PLCB1 and Suppressing DESC1 Expression in MEK1/2 Inhibition-Resistant Cells
- PMID: 34064422
- PMCID: PMC8147860
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10051101
HDAC8 Activates AKT through Upregulating PLCB1 and Suppressing DESC1 Expression in MEK1/2 Inhibition-Resistant Cells
Abstract
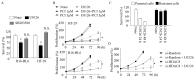
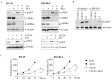
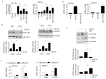
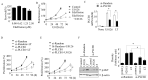
Inhibition of the RAF-MEK1/2-ERK signaling pathway is an ideal strategy for treating cancers with NRAS or BRAF mutations. However, the development of resistance due to incomplete inhibition of the pathway and activation of compensatory cell proliferation pathways is a major impediment of the targeted therapy. The anthrax lethal toxin (LT), which cleaves and inactivates MEKs, is a modifiable biomolecule that can be delivered selectively to tumor cells and potently kills various tumor cells. However, resistance to LT and the mechanism involved are yet to be explored. Here, we show that LT, through inhibiting MEK1/2-ERK activation, inhibits the proliferation of cancer cells with NRAS/BRAF mutations. Among them, the human colorectal tumor HT-29 and murine melanoma B16-BL6 cells developed resistance to LT in 2 to 3 days of treatment. These resistant cells activated AKT through a histone deacetylase (HDAC) 8-dependent pathway. Using an Affymetrix microarray, followed by qPCR validation, we identified that the differential expression of the phospholipase C-β1 (PLCB1) and squamous cell carcinoma-1 (DESC1) played an important role in HDAC8-mediated AKT activation and resistance to MEK1/2-ERK inhibition. By using inhibitors, small interference RNAs and/or expression vectors, we found that the inhibition of HDAC8 suppressed PLCB1 expression and induced DESC1 expression in the resistant cells, which led to the inhibition of AKT and re-sensitization to LT and MEK1/2 inhibition. These results suggest that targeting PLCB1 and DESC1 is a novel strategy for inhibiting the resistance to MEK1/2 inhibition.
Keywords: AKT; DESC1; HT-29 cells; PI-PLC; PLCB1; cancer; lethal toxin; resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Primary cross-resistance to BRAFV600E-, MEK1/2- and PI3K/mTOR-specific inhibitors in BRAF-mutant melanoma cells counteracted by dual pathway blockade.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 26;7(4):3947-65. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6600. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26678033 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic lethal interaction of cetuximab with MEK1/2 inhibition in NRAS-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 13;7(50):82185-82199. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11985. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27636997 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of Mcl-1 confers resistance to BRAFV600E inhibitors alone and in combination with MEK1/2 inhibitors in melanoma.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 1;6(38):40535-56. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5755. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26497853 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting oncogenic Raf protein-serine/threonine kinases in human cancers.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Sep;135:239-258. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.08.013. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 30118796 Review.
-
MEK1/2 Inhibitors: Molecular Activity and Resistance Mechanisms.Semin Oncol. 2015 Dec;42(6):849-62. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2015.09.023. Epub 2015 Sep 24. Semin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26615130 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Competing endogenous RNAs regulatory crosstalk networks: The messages from the RNA world to signaling pathways directing cancer stem cell development.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 26;10(15):e35208. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35208. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNA AC100826.1 regulated PLCB1 to promote progression in non-small cell lung cancer.Thorac Cancer. 2024 Jul;15(19):1477-1489. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15323. Epub 2024 May 22. Thorac Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38778543 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic HDAC4/8 Inhibition Sensitizes Osteosarcoma to Doxorubicin via pAKT/RUNX2 Pathway Modulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 10;26(8):3574. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083574. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332124 Free PMC article.
-
ENO1 promotes liver carcinogenesis through YAP1-dependent arachidonic acid metabolism.Nat Chem Biol. 2023 Dec;19(12):1492-1503. doi: 10.1038/s41589-023-01391-6. Epub 2023 Jul 27. Nat Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37500770
-
Histone deacetylases in the regulation of cell death and survival mechanisms in resistant BRAF-mutant cancers.Cancer Drug Resist. 2025 Jan 25;8:6. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2024.125. eCollection 2025. Cancer Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 39935431 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Noeparast A., Giron P., Noor A., Bahadur Shahi R., De Brakeleer S., Eggermont C., Vandenplas H., Boeckx B., Lambrechts D., De Greve J., et al. Craf mutations in lung cancer can be oncogenic and predict sensitivity to combined type ii raf and mek inhibition. Oncogene. 2019;38:5933–5941. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-0866-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

