BEI Inactivated Vaccine Induces Innate and Adaptive Responses and Elicits Partial Protection upon Reassortant Betanodavirus Infection in Senegalese Sole
- PMID: 34064461
- PMCID: PMC8147993
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9050458
BEI Inactivated Vaccine Induces Innate and Adaptive Responses and Elicits Partial Protection upon Reassortant Betanodavirus Infection in Senegalese Sole
Abstract
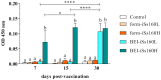
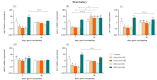
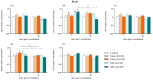
Nervous necrosis virus (NNV), the causative agent of viral encephalopathy and retinopathy (VER), is one of the most threatening viruses affecting marine and freshwater fish species worldwide. Senegalese sole is a promising fish species in Mediterranean aquaculture but also highly susceptible to NNV and VER outbreaks, that puts its farming at risk. The development of vaccines for aquaculture is one of best tools to prevent viral spread and sudden outbreaks, and virus inactivation is the simplest and most cost-effective method available. In this work, we have designed two inactivated vaccines based on the use of formalin or binary ethylenimine (BEI) to inactivate a reassortant NNV strain. After vaccination, the BEI-inactivated vaccine triggered the production of specific IgM-NNV antibodies and stimulated innate and adaptive immune responses at transcriptional level (rtp3, mx, mhcii and tcrb coding genes). Moreover, it partially improved survival after an NNV in vivo challenge, reducing the mid-term viral load and avoiding the down-regulation of immune response post-challenge. On the other hand, the formalin-inactivated vaccine improved the survival of fish upon infection without inducing the production of IgM-NNV antibodies and only stimulating the expression of herc4 and mhcii genes (in head-kidney and brain, respectively) during the vaccination period; this suggests that other immune-related pathways may be involved in the partial protection provoked. Although these vaccines against NNV showed encouraging results, further studies are needed to improve sole protection and to fully understand the underlying immune mechanism.
Keywords: BEI; Senegalese sole; antibodies; formalin; gene expression; immune response; inactivated vaccine; nervous necrosis virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

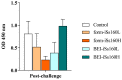
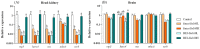
References
-
- FAO . The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture. Opportunities and Challenges. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; Rome, Italy: 2012.
-
- Olveira J.G., Souto S., Dopazo C.P., Thiéry R., Barja J.L., Bandín I. Comparative analysis of both genomic segments of betanodaviruses isolated from epizootic outbreaks in farmed fish species provides evidence for genetic reassortment. J. Gen. Virol. 2009;90:2940–2951. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.013912-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Volpe E., Gustinelli A., Caffara M., Errani F., Quaglio F., Fioravanti M.L., Ciulli S. Viral nervous necrosis outbreaks caused by the RGNNV/SJNNV reassortant betanodavirus in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) and European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Aquaculture. 2020;523:735155. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735155. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

