Metabolic Reprogramming: Strategy for Ischemic Stroke Treatment by Ischemic Preconditioning
- PMID: 34064579
- PMCID: PMC8151271
- DOI: 10.3390/biology10050424
Metabolic Reprogramming: Strategy for Ischemic Stroke Treatment by Ischemic Preconditioning
Abstract
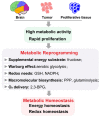
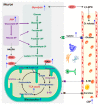
Stroke is one of the leading causes of death and permanent disability worldwide. Ischemic preconditioning (IPC) is an endogenous protective strategy, which has been reported to exhibit a significant neuroprotective effect in reducing the incidence of ischemic stroke. However, the underlying neuroprotective mechanisms of IPC remain elusive. An increased understanding of the pathogenic mechanisms of stroke and IPC serves to highlight the importance of metabolic reprogramming. In this review, we summarize the metabolic disorder and metabolic plasticity in the incidence and progression of ischemic stroke. We also elaborate how IPC fully mobilizes the metabolic reprogramming to maintain brain metabolic homeostasis, especially for energy and redox homeostasis, and finally protects brain function in the event of an ischemic stroke.
Keywords: ischemic preconditioning (IPC); ischemic stroke; metabolic reprogramming.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Zhou M., Wang H., Zeng X., Yin P., Zhu J., Chen W., Li X., Wang L., Wang L., Liu Y., et al. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2019;394:1145–1158. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30427-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen S.Y., Liu J.W., Wang Y.H., Huang J.Y., Chen S.C., Yang S.F., Wang P.H. The Conditions Under Which Piracetam Is Used and the Factors That Can Improve National Institute of Health Stroke Scale Score in Ischemic Stroke Patients and the Importance of Previously Unnoticed Factors from a Hospital-Based Observational Study in Taiwan. J. Clin. Med. 2019;8:122. doi: 10.3390/jcm8010122. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

