The RNA-Binding Protein HuD Regulates Alternative Splicing and Alternative Polyadenylation in the Mouse Neocortex
- PMID: 34064652
- PMCID: PMC8151252
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26102836
The RNA-Binding Protein HuD Regulates Alternative Splicing and Alternative Polyadenylation in the Mouse Neocortex
Abstract
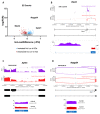
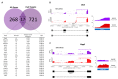
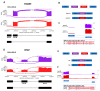
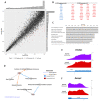
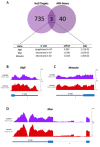
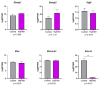
The neuronal Hu/ELAV-like proteins HuB, HuC and HuD are a class of RNA-binding proteins that are crucial for proper development and maintenance of the nervous system. These proteins bind to AU-rich elements (AREs) in the untranslated regions (3'-UTRs) of target mRNAs regulating mRNA stability, transport and translation. In addition to these cytoplasmic functions, Hu proteins have been implicated in alternative splicing and alternative polyadenylation in the nucleus. The purpose of this study was to identify transcriptome-wide effects of HuD deletion on both of these nuclear events using RNA sequencing data obtained from the neocortex of Elavl4-/- (HuD KO) mice. HuD KO affected alternative splicing of 310 genes, including 17 validated HuD targets such as Cbx3, Cspp1, Snap25 and Gria2. In addition, deletion of HuD affected polyadenylation of 53 genes, with the majority of significantly altered mRNAs shifting towards usage of proximal polyadenylation signals (PAS), resulting in shorter 3'-UTRs. None of these genes overlapped with those showing alternative splicing events. Overall, HuD KO had a greater effect on alternative splicing than polyadenylation, with many of the affected genes implicated in several neuronal functions and neuropsychiatric disorders.
Keywords: Elavl4 KO; HuD; alternative polyadenylation; alternative splicing; neocortex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

