Effectiveness of a New Recombinant antiGnRH Vaccine for Immunocastration in Bulls
- PMID: 34064713
- PMCID: PMC8151010
- DOI: 10.3390/ani11051359
Effectiveness of a New Recombinant antiGnRH Vaccine for Immunocastration in Bulls
Abstract
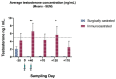
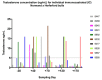
Castration by surgical techniques is common in livestock; however, post-surgery complications and concerns for animal wellbeing have created a need for new non-invasive alternatives. The objective of this study was to evaluate immunocastration in bulls using antigen GnRX G/Q; a recombinant peptide proved to be effective in laboratory and companion animals. A nine-month trial with 80 9-month-old Normand x Hereford bulls, kept in a pastured system, was conducted. The herd was divided in half with 40 bulls surgically castrated (SC) and 40 castrated by immunization against GnRH (IC). The antigen was injected on days 0 and 40 of the experiment. After the second dose, the IC group had elevated GnRH antibodies and decreased testosterone levels (below 5 ng/mL) that were maintained for 23 weeks. At slaughter on day 190, the immunocastrated group obtained a higher weight, hot carcass, and dressing percentage than the SC group. There was no difference in pH, color of meat, fat coverage, cooking loss, or tenderness between groups. The bulls showed no inflammatory reaction at the injection site or adverse side effects from the vaccine. Our results demonstrate that immunocastration with GnRX G/Q is an efficient and safe alternative to surgical castration in livestock. Additional work evaluating antigen effects over a longer period is needed to validate commercial viability.
Keywords: GnRH antibodies; immunocastration; livestock; meat quality; recombinant vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
GnRH-immunocastration: an alternative method for male animal surgical castration.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Oct 31;10:1248879. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1248879. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 38026623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects on performance and carcass and meat quality attributes following immunocastration with the gonadotropin releasing factor vaccine Bopriva or surgical castration of Bos indicus bulls raised on pasture in Brazil.Meat Sci. 2013 Sep;95(1):78-84. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2013.04.008. Epub 2013 Apr 15. Meat Sci. 2013. PMID: 23665362
-
Growth and carcass characteristics of pasture fed LHRH immunocastrated, castrated and intact Bos indicus bulls.Meat Sci. 2004 Oct;68(2):285-90. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2004.03.008. Meat Sci. 2004. PMID: 22062238
-
Efficiency of immunocastration with an anti-gonadotropin-releasing hormone vaccine on cryptorchid bulls.J Vet Med Sci. 2023 May 3;85(5):551-556. doi: 10.1292/jvms.22-0571. Epub 2023 Mar 16. J Vet Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36927961 Free PMC article.
-
New trends in immunocastration and its potential to improve animal welfare: a mini review.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2022 Nov 2;54(6):369. doi: 10.1007/s11250-022-03348-8. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2022. PMID: 36323906 Review.
Cited by
-
GnRH-immunocastration: an alternative method for male animal surgical castration.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Oct 31;10:1248879. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1248879. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 38026623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improving Beef Cattle Production: Safety and Effectiveness of New Immunocastration Vaccine.Animals (Basel). 2024 Aug 31;14(17):2538. doi: 10.3390/ani14172538. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272323 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Vaccine Formulation for Immunocastration Using a Live-Attenuated Salmonella ΔSPI2 Strain as an Antigenic Vector.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Dec 12;12(12):1400. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12121400. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39772060 Free PMC article.
-
Delivering an Immunocastration Vaccine via a Novel Subcutaneous Implant.Animals (Basel). 2022 Oct 7;12(19):2698. doi: 10.3390/ani12192698. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230439 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pang W., Earley B., Gath V., Crowe M. Effect of banding or burdizzo castration on plasma testosterone, acute-phase proteins, scrotal circumference, growth, and health of bulls. Livest. Sci. 2008;117:79–87. doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2007.11.012. - DOI
-
- Amatayakul-Chantler S., Hoe F., Jackson J., Roca R., Stegner J., King V., Howard R., Lopez E., Walker J. Effects on performance and carcass and meat quality attributes following immunocastration with the gonadotropin releasing factor vaccine Bopriva or surgical castration of Bos indicus bulls raised on pasture in Brazil. Meat Sci. 2013;95:78–84. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2013.04.008. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

