Anthracyclins Increase PUFAs: Potential Implications in ER Stress and Cell Death
- PMID: 34064765
- PMCID: PMC8151859
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10051163
Anthracyclins Increase PUFAs: Potential Implications in ER Stress and Cell Death
Abstract
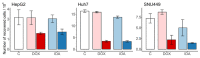
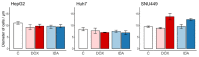
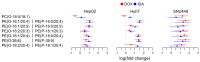
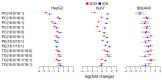
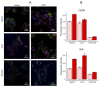
Metabolic and personalized interventions in cancer treatment require a better understanding of the relationship between the induction of cell death and metabolism. Consequently, we treated three primary liver cancer cell lines with two anthracyclins (doxorubicin and idarubin) and studied the changes in the lipidome. We found that both anthracyclins in the three cell lines increased the levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) and alkylacylglycerophosphoethanolamines (etherPEs) with PUFAs. As PUFAs and alkylacylglycerophospholipids with PUFAs are fundamental in lipid peroxidation during ferroptotic cell death, our results suggest supplementation with PUFAs and/or etherPEs with PUFAs as a potential general adjuvant of anthracyclins. In contrast, neither the markers of de novo lipogenesis nor cholesterol lipids presented the same trend in all cell lines and treatments. In agreement with previous research, this suggests that modulation of the metabolism of cholesterol could be considered a specific adjuvant of anthracyclins depending on the type of tumor and the individual. Finally, in agreement with previous research, we found a relationship across the different cell types between: (i) the change in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, and (ii) the imbalance between PUFAs and cholesterol and saturated lipids. In the light of previous research, this imbalance partially explains the sensitivity to anthracyclins of the different cells. In conclusion, our results suggest that the modulation of different lipid metabolic pathways may be considered for generalized and personalized metabochemotherapies.
Keywords: ferroptosis; hepatocellular carcinoma; lipidomics; plasmalogen; plasmanyl; plasmenyl.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Smith M.R., Chacko B.K., Johnson M.S., Benavides G.A., Uppal K., Go Y.-M., Jones D.P., Darley-Usmar V.M. A Precision Medicine Approach to Defining the Impact of Doxorubicin on the Bioenergetic-Metabolite Interactome in Human Platelets. Redox Biol. 2020;28:101311. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101311. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

