Classification of Chronic Kidney Disease in Sonography Using the GLCM and Artificial Neural Network
- PMID: 34064910
- PMCID: PMC8151922
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11050864
Classification of Chronic Kidney Disease in Sonography Using the GLCM and Artificial Neural Network
Abstract
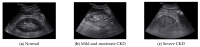
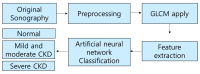
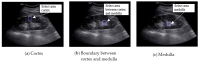
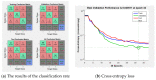
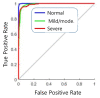
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) can be treated if it is detected early, but as the disease progresses, recovery becomes impossible. Eventually, renal replacement therapy such as transplantation or dialysis is necessary. Ultrasound is a test method with which to diagnose kidney cancer, inflammatory disease, nodular disease, chronic kidney disease, etc. It is used to determine the degree of inflammation using information such as the kidney size and internal echo characteristics. The degree of the progression of chronic kidney disease in the current clinical trial is based on the value of the glomerular filtration rate. However, changes in the degree of inflammation and disease can even be observed with ultrasound. In this study, from a total of 741 images, 251 normal kidney images, 328 mild and moderate CKD images, and 162 severe CKD images were tested. In order to diagnose CKD in clinical practice, three ROIs were set: the cortex of the kidney, the boundary between the cortex and medulla, and the medulla, which are areas examined to obtain information from ultrasound images. Parameters were extracted from each ROI using the GLCM algorithm, which is widely used in ultrasound image analysis. When each parameter was extracted from the three areas, a total of 57 GLCM parameters were extracted. Finally, a total of 58 parameters were used by adding information on the size of the kidney, which is important for the diagnosis of chronic kidney disease. The artificial neural network (ANN) was composed of 58 input parameters, 10 hidden layers, and 3 output layers (normal, mild and moderate CKD, and severe CKD). Using the ANN model, the final classification rate was 95.4%, the epoch needed for training was 38 times, and the misclassification rate was 4.6%.
Keywords: artificial neural network; chronic kidney disease (CKD); classification; gray-level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM); kidney ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Improved glomerular filtration rate estimation by an artificial neural network.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58242. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058242. Epub 2013 Mar 13. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23516450 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Muscle Ultrasonography Using 2D Textural Analysis: A Novel Approach to Assess Skeletal Muscle Structure and Quality in Chronic Kidney Disease.Ultrason Imaging. 2021 May;43(3):139-148. doi: 10.1177/01617346211009788. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Ultrason Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33853450 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of the performances of an artificial neural network and a regression model for GFR estimation.Am J Kidney Dis. 2013 Dec;62(6):1109-15. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.07.010. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013. PMID: 24011972
-
Exploration of a Framework for the Identification of Chronic Kidney Disease Based on 2D Ultrasound Images: A Survey.Curr Med Imaging. 2021;17(4):464-478. doi: 10.2174/1573405616666200923162600. Curr Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 32964826
-
Clinical epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease prior to dialysis.Semin Dial. 2003 Mar-Apr;16(2):101-5. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-139x.2003.16025.x. Semin Dial. 2003. PMID: 12641872 Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial intelligence in glomerular diseases.Pediatr Nephrol. 2022 Nov;37(11):2533-2545. doi: 10.1007/s00467-021-05419-8. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Pediatr Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35266037 Review.
-
Towards Accurate Diagnosis of Skin Lesions Using Feedforward Back Propagation Neural Networks.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 May 22;11(6):936. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11060936. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34067493 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced ultrasound methods to improve chronic kidney disease diagnosis.Npj Imaging. 2024 Jul 25;2(1):22. doi: 10.1038/s44303-024-00023-5. Npj Imaging. 2024. PMID: 40604097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease Using Effective Classification Algorithms and Recursive Feature Elimination Techniques.J Healthc Eng. 2021 Jun 9;2021:1004767. doi: 10.1155/2021/1004767. eCollection 2021. J Healthc Eng. 2021. PMID: 34211680 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence-aided ultrasound in renal diseases: a systematic review.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Jun 1;13(6):3988-4001. doi: 10.21037/qims-22-1428. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 37284081 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lovey A.S., Eckardt K.U., Tsukamoto Y., Levin A., Coresh J., Rossert J., de Zeeuw D., Hostetter T.H., Lameire N., Eknoyan G. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: A position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes(KDIGO) Kidney Int. 2005;67:2089–2100. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00365.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

