Correlation between Elderly Migrants' Needs and Environmental Adaptability: A Discussion Based on Human Urbanization Features
- PMID: 34064998
- PMCID: PMC8150798
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18105068
Correlation between Elderly Migrants' Needs and Environmental Adaptability: A Discussion Based on Human Urbanization Features
Abstract
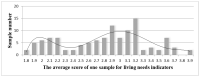
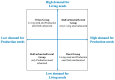
Building concentrated resettlement community in small towns is mostly used to deal with resettlement construction for rural migrants in economically developed regions in China, which leads to migrants' living environment changing from rural settlements where production and living are intertwined to an urban community that only supports living functions. However, the urbanized environment is contrary to elderly migrants' behavior, resulting in contradictions or conflicts between migrants and resettlement communities, reflecting a lack of urbanization synchronization between migrants and resettlement community environments. Further, elderly migrants are also equipped with different degrees and types of urbanization characteristics, thus reflecting different abilities to adapt to the urban community environment. Based on the corresponding relationship between people's different production and living needs and urbanization, this research starts by investigating the production and living needs of elderly migrants, and further clarifies the environmental adaptability of elderly migrants by sorting the types and characteristics of urbanization of elderly migrants to provide a reference basis for the planning and construction of future resettlement areas. The research uses questionnaires and semi-structured interviews to investigate the population attributes and characteristics of elderly migrants, as well as their different needs for production and living. The research uses hierarchical cluster analysis, the one-way ANOVA test and Chi-square test to constructed a four-quadrant model on human urbanization features: an Urban Group with both living and production urbanized (Group H-H); a Half-urban-half-rural Group with only living needs urbanized (Group H-L); a Half-urban-Half-rural Group with only production needs urbanized (Group L-H); and a Rural group with both living and production needs not urbanized (Group L-L). Finally, based on the results, this research proposed three elderly environment construction orientations of "Promote the Supply Level of Urban Public Services", "Create a Place That Embodies the Spirit of Immigrants' Homeland", and "Moderate Consideration of Agricultural Production Needs" for residential planning.
Keywords: elderly migrant; environmental adaptability; human urbanization feature; living need; production need.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Tang S., Hao P., Huang X. Land conversion and urban settlement intentions of the rural population in China: A case study of suburban Nanjing. Habitat Int. 2016;51:149–158. doi: 10.1016/j.habitatint.2015.10.023. - DOI
-
- Yang Q., Ley D. Residential relocation and the remaking of socialist workers through state-facilitated urban redevelopment in Chengdu, China. Urban. Stud. 2019;56:2480–2498. doi: 10.1177/0042098018790724. - DOI
-
- Yi Z., Gu M. Planning and practice of reservoir resettlement in new-type urbanization mode: Case of Nan’an Reservoir in Yongjia County of Wenzhou City. Yangtze River. 2015;46:107–111. (In Chinese)
-
- Lian H., Glendinning A., Yin B. The Issue of ‘Land-lost’ Farmers in the People’s Republic of China: Reasons for discontent, actions and claims to legitimacy. J. Contemp. China. 2016;25:718–730. doi: 10.1080/10670564.2016.1160505. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

