Genomic Characterisation of a Novel Avipoxvirus Isolated from an Endangered Northern Royal Albatross (Diomedea sanfordi)
- PMID: 34065100
- PMCID: PMC8151833
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens10050575
Genomic Characterisation of a Novel Avipoxvirus Isolated from an Endangered Northern Royal Albatross (Diomedea sanfordi)
Abstract
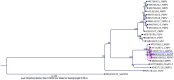
Marine bird populations have been declining globally with the factors driving this decline not fully understood. Viral diseases, including those caused by poxviruses, are a concern for endangered seabird species. In this study we have characterised a novel avipoxvirus, tentatively designated albatrosspox virus (ALPV), isolated from a skin lesion of an endangered New Zealand northern royal albatross (Diomedea sanfordi). The ALPV genome was 351.9 kbp in length and contained 336 predicted genes, seven of which were determined to be unique. The highest number of genes (313) in the ALPV genome were homologs of those in shearwaterpox virus 2 (SWPV2), while a further 10 were homologs to canarypox virus (CNPV) and an additional six to shearwaterpox virus 1 (SWPV1). Phylogenetic analyses positioned the ALPV genome within a distinct subclade comprising recently isolated avipoxvirus genome sequences from shearwater, penguin and passerine bird species. This is the first reported genome sequence of ALPV from a northern royal albatross and will help to track the evolution of avipoxvirus infections in this endangered species.
Keywords: avipoxvirus; complete genome; endangered; evolution; northern royal albatross.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evidence of a Possible Viral Host Switch Event in an Avipoxvirus Isolated from an Endangered Northern Royal Albatross (Diomedea sanfordi).Viruses. 2022 Feb 1;14(2):302. doi: 10.3390/v14020302. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215898 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Characterisation of a Novel Avipoxvirus Isolated from an Endangered Yellow-Eyed Penguin (Megadyptes antipodes).Viruses. 2021 Jan 28;13(2):194. doi: 10.3390/v13020194. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33525382 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic characterization of two novel pathogenic avipoxviruses isolated from pacific shearwaters (Ardenna spp.).BMC Genomics. 2017 Apr 13;18(1):298. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3680-z. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28407753 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterisation of a novel pathogenic avipoxvirus from an Australian passerine bird, mudlark (Grallina cyanoleuca).Virology. 2021 Feb;554:66-74. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2020.12.011. Epub 2020 Dec 28. Virology. 2021. PMID: 33385935
-
Longline fishing (how what you don't know can hurt you).Top Companion Anim Med. 2013 Nov;28(4):151-62. doi: 10.1053/j.tcam.2013.09.006. Top Companion Anim Med. 2013. PMID: 24331555 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular characterisation of a novel pathogenic avipoxvirus from an Australian little crow (Corvus bennetti) directly from the clinical sample.Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 5;12(1):15053. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-19480-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36064742 Free PMC article.
-
A novel variant of Babesia sp. (Piroplasmida) as a hemoparasite in procellariiform seabirds.Parasitol Res. 2023 Aug;122(8):1935-1941. doi: 10.1007/s00436-023-07894-4. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Parasitol Res. 2023. PMID: 37314510
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of microsatellite markers within the Avipoxviruses.3 Biotech. 2022 May;12(5):113. doi: 10.1007/s13205-022-03169-4. Epub 2022 Apr 13. 3 Biotech. 2022. PMID: 35497507 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Pathogenic Avipoxvirus Infecting Vulnerable Cook's Petrel (Pterodroma cookii) in Australia Demonstrates a High Genomic and Evolutionary Proximity with South African Avipoxviruses.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 7;11(2):e0461022. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04610-22. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36749064 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of a Possible Viral Host Switch Event in an Avipoxvirus Isolated from an Endangered Northern Royal Albatross (Diomedea sanfordi).Viruses. 2022 Feb 1;14(2):302. doi: 10.3390/v14020302. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Croxall J.P., Butchart S.H.M., Lascelles B.E.N., Stattersfield A.J., Sullivan B.E.N., Symes A., Taylor P. Seabird conservation status, threats and priority actions: A global assessment. Bird Conserv. Int. 2012;22:1–34. doi: 10.1017/S0959270912000020. - DOI
-
- Croxall J.P., Gales R. An assessment of the conservation status of albatrosses. In: Robertson G., Gales R., editors. Albatross Biology and Conservation. Surrey Beatty & Sons; Chipping Norton, UK: 1998. pp. 46–65.
-
- Cooper J., Baker G.B., Double M.C., Gales R., Papworth W., Tasker M.L., Waugh S.M. The agreement on the conservation of albatrosses and petrels: Rationale, history, progress and the way forward. Mar. Ornithol. 2006;34:1–5.
-
- Marcela M., Uhart L.G., Flavio Q. Review of diseases (pathogen isolation, direct recovery and antibodies) in albatrosses and large petrels worldwide. Bird Conserv. Int. 2017;28:1–28. doi: 10.1017/S0959270916000629. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

