Biological Functions of Rat Ultrasonic Vocalizations, Arousal Mechanisms, and Call Initiation
- PMID: 34065107
- PMCID: PMC8150717
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci11050605
Biological Functions of Rat Ultrasonic Vocalizations, Arousal Mechanisms, and Call Initiation
Abstract
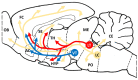
This review summarizes all reported and suspected functions of ultrasonic vocalizations in infant and adult rats. The review leads to the conclusion that all types of ultrasonic vocalizations subserving all functions are vocal expressions of emotional arousal initiated by the activity of the reticular core of the brainstem. The emotional arousal is dichotomic in nature and is initiated by two opposite-in-function ascending reticular systems that are separate from the cognitive reticular activating system. The mesolimbic cholinergic system initiates the aversive state of anxiety with concomitant emission of 22 kHz calls, while the mesolimbic dopaminergic system initiates the appetitive state of hedonia with concomitant emission of 50 kHz vocalizations. These two mutually exclusive arousal systems prepare the animal for two different behavioral outcomes. The transition from broadband infant isolation calls to the well-structured adult types of vocalizations is explained, and the social importance of adult rat vocal communication is emphasized. The association of 22 kHz and 50 kHz vocalizations with aversive and appetitive states, respectively, was utilized in numerous quantitatively measured preclinical models of physiological, psychological, neurological, neuropsychiatric, and neurodevelopmental investigations. The present review should help in understanding and the interpretation of these models in biomedical research.
Keywords: 22 kHz calls; 50 kHz calls; anxiety; emotional arousal; evolution of vocalization; hedonia; infant isolation calls; mesolimbic cholinergic system; mesolimbic dopaminergic system; rat; ultrasonic vocalization.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacology of Ultrasonic Vocalizations in adult Rats: Significance, Call Classification and Neural Substrate.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2015;13(2):180-92. doi: 10.2174/1570159x13999150210141444. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26411761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The antagonistic relationship between aversive and appetitive emotional states in rats as studied by pharmacologically-induced ultrasonic vocalization from the nucleus accumbens and lateral septum.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2019 Jun;181:77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2019.04.009. Epub 2019 Apr 26. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2019. PMID: 31034853
-
Communication of adult rats by ultrasonic vocalization: biological, sociobiological, and neuroscience approaches.ILAR J. 2009;50(1):43-50. doi: 10.1093/ilar.50.1.43. ILAR J. 2009. PMID: 19106451
-
Ethotransmission: communication of emotional states through ultrasonic vocalization in rats.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013 Jun;23(3):310-7. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2013.01.014. Epub 2013 Jan 31. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23375168 Review.
-
Male rats emit aversive 44-kHz ultrasonic vocalizations during prolonged Pavlovian fear conditioning.Elife. 2024 Dec 10;12:RP88810. doi: 10.7554/eLife.88810. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39656518 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of reduced kinematic and social play experience on affective appraisal of human-rat play in rats.Front Zool. 2023 Oct 12;20(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12983-023-00512-0. Front Zool. 2023. PMID: 37821980 Free PMC article.
-
Playback of rat 22-kHz ultrasonic vocalizations as a translational assay of negative affective states: An analysis of evoked behavior and brain activity.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2023 Oct;153:105396. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2023.105396. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2023. PMID: 37739328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Response Calls Evoked by Playback of Natural 50-kHz Ultrasonic Vocalizations in Rats.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Jan 14;15:812142. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2021.812142. eCollection 2021. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35095442 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in fear responses: Neural circuits.Neuropharmacology. 2023 Jan 1;222:109298. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2022.109298. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Neuropharmacology. 2023. PMID: 36328063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early ultrasonic vocalization deficits and related thyroarytenoid muscle pathology in the transgenic TgF344-AD rat model of Alzheimer's disease.Front Behav Neurosci. 2024 Jan 23;17:1294648. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2023.1294648. eCollection 2023. Front Behav Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38322496 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

